HTHQ
CAS No. 148081-72-5
HTHQ( HX-1171 | HX-1171 | HX-1171 | HTHQ )
Catalog No. M18047 CAS No. 148081-72-5
HTHQ, a hydroquinone monoalkyl ether, is an effective anti-oxidative agent.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 142 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameHTHQ
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionHTHQ, a hydroquinone monoalkyl ether, is an effective anti-oxidative agent.
-
DescriptionHX-1171, also known as HTHQ, is a lipid peroxidation inhibitor potentially for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis. HTHQ and vitamin E attenuated interleukin-1beta-induced iNOS protein expression in cultured hepatocytes, the potency of HTHQ being 10-times higher than that of vitamin E. HTHQ may prevent tumor production induced by AP and NaNO2 more effectively than ascorbic acid.(In Vitro):HTHQ (0-100 μM; 24 hours; PC12 cells) treatment increases cell viabilities in a dose-dependent manner.HTHQ (10 μM; 0.6-24 hours; PC12 cells) inhibits 3,4-L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) -induced phosphorylation of sustaines extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1/2). HTHQ also normalizes L-DOPA-reduced Bcl-2-associated death protein (Bad) phosphorylation and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) expression, promoting cell survival.(In Vivo):HTHQ (50-200 mg/kg; oral administration; for 4 weeks; specific pathogen-free male Sprague Dawley rats) treatment significantly improves liver weight and serum chemistry level. HTHQ reduces hydroxyproline and malondialdehyde level in the liver. HTHQ treatment also reduces fibrotic septa. HTHQ administration shows reduced mRNA level of PDGF (Plateletderived growth factor) , α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin) and TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) than DMN-induced hepetic fibrosis animals in the liver tissue.
-
In VitroHTHQ (0-100 μM; 24 hours; PC12 cells) treatment increases cell viabilities in a dose-dependent manner.HTHQ (10 μM; 0.6-24 hours; PC12 cells) inhibits 3,4-L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) -induced phosphorylation of sustaines extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1/2). HTHQ also normalizes L-DOPA-reduced Bcl-2-associated death protein (Bad) phosphorylation and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) expression, promoting cell survival. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:PC12 cells Concentration:0 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, and 100 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Reduced cell viability at 24 hours caused by both 100 and 200 μM L-DOPA was significantly attenuated.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:PC12 cells Concentration:10 μM Incubation Time:0.6-24 hours Result:Inhibited L-DOPA-induced phosphorylation of sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1/2). And also normalized L-DOPA-reduced Bcl-2-associated death protein (Bad) phosphorylation and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) expression.
-
In VivoHTHQ (50-200 mg/kg; oral administration; for 4 weeks; specific pathogen-free male Sprague Dawley rats) treatment significantly improves liver weight and serum chemistry level. HTHQ reduces hydroxyproline and malondialdehyde level in the liver. HTHQ treatment also reduces fibrotic septa. HTHQ administration shows reduced mRNA level of PDGF (Plateletderived growth factor) , α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin) and TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) than DMN-induced hepetic fibrosis animals in the liver tissue. Animal Model:48 specific pathogen-free male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (6-week-old ) with dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) Dosage:50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg Administration:Oral administration; for 4 weeks Result:Improved against DMN-induced liver fibrosis in male SD rats.
-
SynonymsHX-1171 | HX-1171 | HX-1171 | HTHQ
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number148081-72-5
-
Formula Weight236.35
-
Molecular FormulaC15H24O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 423.10 mM
-
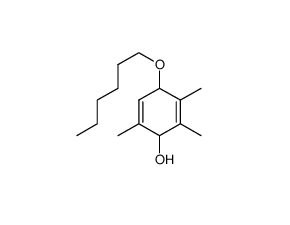
SMILESCCCCCCOc1c(c(c(c(c1)C)O)C)C
-
Chemical Name4-(hexyloxy)-2,3,6-trimethylphenol
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hino T, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Sep 16;1425(1):47-60.
molnova catalog



related products
-
KK4A
KK4A
-
Secretin (28-54), hu...
Secretin (28-54), human, which acts on human secretin receptors, is a 27-amino acid residue C-terminally amidated peptide, .
-
Tau-aggregation and ...
Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of tau protein aggregates, showing significant inhibitory activity against AcPHF6 and full-length tau protein aggregates.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


