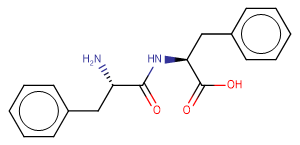
H-Phe-Phe-OH
CAS No. 2577-40-4
H-Phe-Phe-OH( —— )
Catalog No. M21422 CAS No. 2577-40-4
H-Phe-Phe-OH is a peptide made of two phenylalanine molecules; Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid and the precursor for the amino acid tyrosine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameH-Phe-Phe-OH
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionH-Phe-Phe-OH is a peptide made of two phenylalanine molecules; Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid and the precursor for the amino acid tyrosine.
-
DescriptionH-Phe-Phe-OH is a peptide made of two phenylalanine molecules; Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid and the precursor for the amino acid tyrosine.
-
In VitroH-Phe-Phe-OH (Phe-Phe) is a peptide made of two phenylalanine molecules. Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid and the precursor for the amino acid tyrosine. It is the precursor of catecholamines in the body. The psychotropic drugs also have phenylalanine as a constituent. The H-Phe-Phe-OH recognition motif of the Alzheimer's Abeta peptide is the smallest peptide able to assemble into higher -order structures.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2577-40-4
-
Formula Weight312.36
-
Molecular FormulaC18H20N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?80% Acetic acid/water : 50 mg/)
-
SMILESN[C@@H](Cc1ccccc1)C(N[C@@H](Cc1ccccc1)C(O)=O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.de Groot NS et al. Ile-phe dipeptide self-assembly: clues to amyloid formation. Biophys J. 2007 Mar 1;92(5):1732-41.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Flavin adenine dinuc...
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a REDOX cofactor and protein cogroup involved in various metabolic reactions.
-
L-Galactose
L-Galactose (Galactose, L-) is a natural product that is widely found in plants and animals. L-Galactose has been shown to be a key intermediate in the molecular pathway for the conversion of D-glucose to oxalic acid in Pistia stratiotes.
-
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleri...
3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. 3-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid is a neurotoxin an acidogen and a metabotoxin. A neurotoxin causes damage to nerve cells and nerve tissues.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


