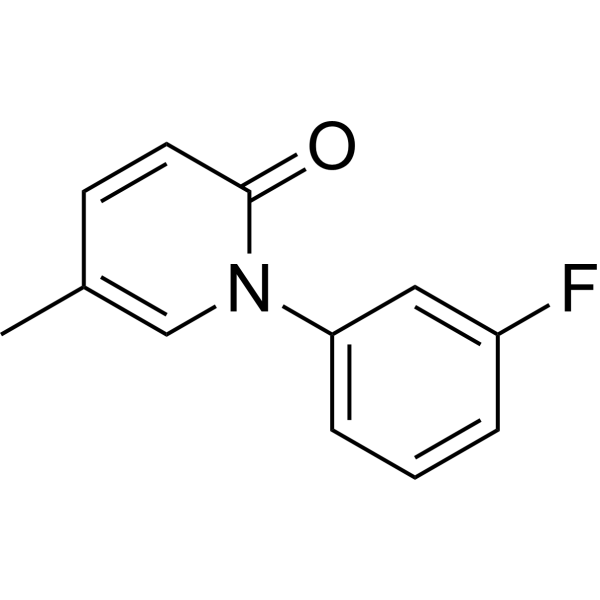
Fluorofenidone
CAS No. 848353-85-5
Fluorofenidone( AKF-PD )
Catalog No. M26688 CAS No. 848353-85-5
Fluorofenidone attenuates the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis partly by suppressing NADPH oxidase and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition via the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 53 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 147 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 295 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 514 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 737 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1521 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFluorofenidone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFluorofenidone attenuates the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis partly by suppressing NADPH oxidase and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition via the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway.
-
DescriptionFluorofenidone attenuates the progression of renal interstitial fibrosis partly by suppressing NADPH oxidase and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition via the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Fluorofenidone is an analogue of AMR69. Which displays equivalent lower toxicity, antifibrotic activity, and longer half-life.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAKF-PD
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number848353-85-5
-
Formula Weight203.216
-
Molecular FormulaC12H10FNO
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 140 mg/mL (688.94 mM)
-
SMILESCc1ccc(=O)n(c1)-c1cccc(F)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Shi J, et al. Sacubitril Is Selectively Activated by Carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) in the Liver and the Activation Is Affected by CES1 Genetic Variation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Apr;44(4):554-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Skp2 inhibitor 1
Skp2 inhibitor 1 is a Skp2-Cks1 interaction inhibitor (IC50: 2.8μM) with antitumor activity and can be used to study cancer.
-
5-Hydroxy-7-(4-hydro...
5-Hydroxy-7-(4'-hydroxy-3'-methoxyphenyl)-1-phenyl-3-heptanone (DHPA) is a pancreatic lipase inhibitor, it shows antihyperlipidemic activity.
-
Uridine
Uridine, Trisodium Salt is an energy-rich precursor in the enzymatic biosynthesis of RNA, a potent vasodilator, and induces contractile responses in some tissues.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


