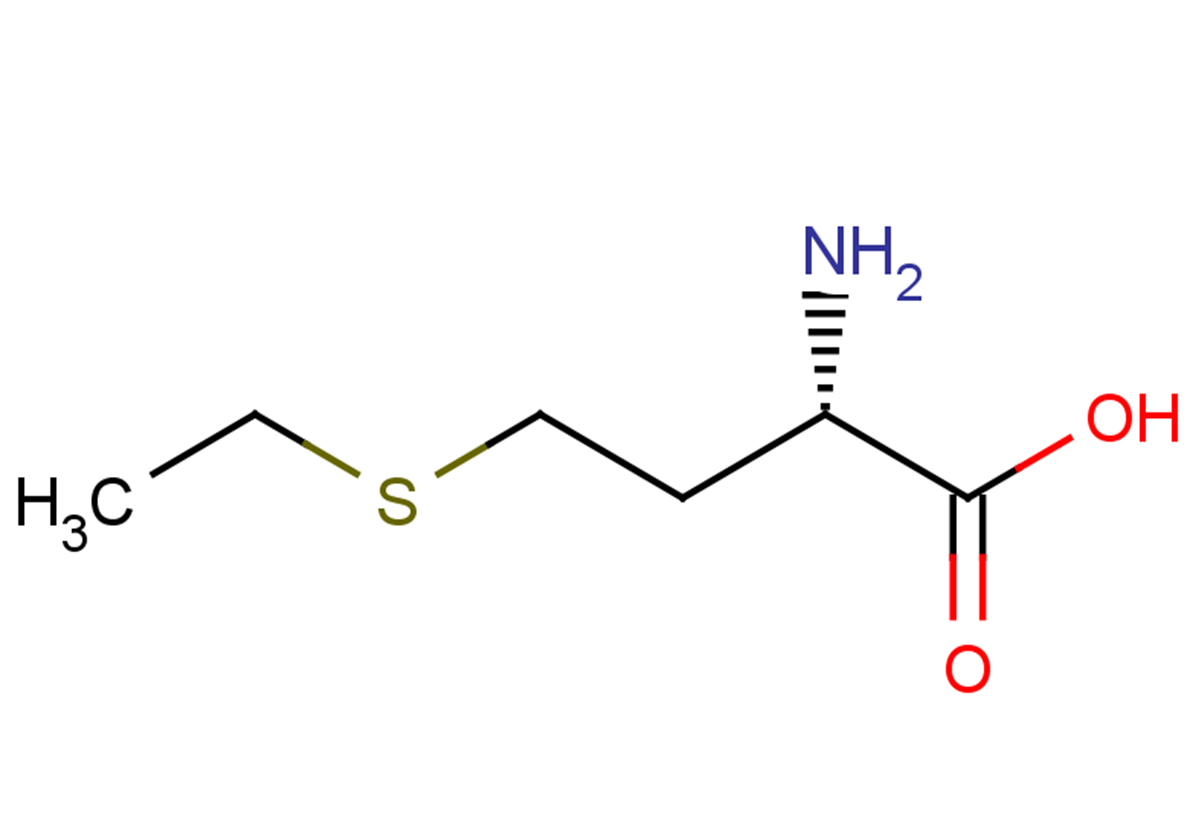
Ethionine
CAS No. 13073-35-3
Ethionine( L-Ethionine | ETH | NSC 82393 | NSC-82393 | NSC82393 )
Catalog No. M23462 CAS No. 13073-35-3
Ethionine is an antimetabolite and methionine antagonist. It also produces liver neoplasms.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 86 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 122 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 176 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 258 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEthionine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEthionine is an antimetabolite and methionine antagonist. It also produces liver neoplasms.
-
DescriptionEthionine is an antimetabolite and methionine antagonist. It also produces liver neoplasms.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsL-Ethionine | ETH | NSC 82393 | NSC-82393 | NSC82393
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number13073-35-3
-
Formula Weight163.23
-
Molecular FormulaC6H13NO2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Soluble
-
SMILESCCSCC[C@@H](C(O)=O)N
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Khambu B, Huda N, Chen X, Antoine DJ, Li Y, Dai G, K?hler UA, Zong WX, Waguri S, Werner S, Oury TD, Dong Z, Yin XM. HMGB1 promotes ductular reaction and tumorigenesis in autophagy-deficient livers. J Clin Invest. 2018 May 7. pii: 91814. doi: 10.1172/JCI91814. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 29558368.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Cisd2 agonist 1
Cisd2 agonist 1 is a potent CDGSH iron-sulfur structural domain 2 (CISD2) agonist (EC50: 34 nM) with potential anticancer activity for the study of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
-
PBT-1033
PBT-1033(PBT-2) is a potential neuroprotective agent for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease.
-
Prolyl-4-hydroxylase...
Prolyl-4-hydroxylase Inhibitor 11, a novel proline 4-hydroxylase inhibitor, shows protective effects against oxidative stress and Cu(II) toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


