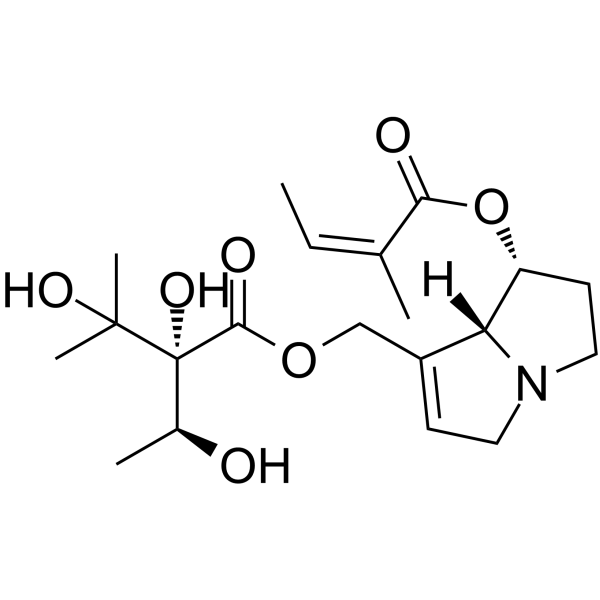
Echimidine
CAS No. 520-68-3
Echimidine( —— )
Catalog No. M31037 CAS No. 520-68-3
Echimidine, a major hepatotoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by E. plantagineum, in the honey (780 ng/g) and in the subsequent mead samples (236-540 ng/mL). Echimidine-N-Oxide has antifungal activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 835 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEchimidine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEchimidine, a major hepatotoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by E. plantagineum, in the honey (780 ng/g) and in the subsequent mead samples (236-540 ng/mL). Echimidine-N-Oxide has antifungal activity.
-
DescriptionEchimidine, a major hepatotoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by E. plantagineum, in the honey (780 ng/g) and in the subsequent mead samples (236-540 ng/mL). Echimidine-N-Oxide has antifungal activity.
-
In VitroEchimidine, a major hepatotoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by E. plantagineum, in the honey (780 ng/g) and in the subsequent mead samples (236-540 ng/mL).
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number520-68-3
-
Formula Weight397.47
-
Molecular FormulaC20H31NO7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Betulinic acid methy...
Betulinic acid methyl ester showed antiplasmodial activity against chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum parasites in vitro.It also inhibited B16 2F2 cell proliferation by induction of apoptosis.
-
PJ34
PJ34 HCl is the hydrochloride salt of PJ34, which is a PARP inhibitor with EC50 of 20 nM and is equally potent to PARP1/2.
-
Pentamidine isethion...
Pentamidine isethionate is an antimicrobial agent for prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


