Dyngo-4a
CAS No. 1256493-34-1
Dyngo-4a( Dyngo-49 | Dyngo 49 | Hydroxy Dynasore )
Catalog No. M17909 CAS No. 1256493-34-1
Dyngo-4a , a effective dynamin inhibitor, inhibits withDynI (brain), DynI (rec), and DynII (rec) of IC50 of 0.38 μM, 1.1 μM, and 2.3 μM, respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 210 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 312 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 464 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 743 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDyngo-4a
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDyngo-4a , a effective dynamin inhibitor, inhibits withDynI (brain), DynI (rec), and DynII (rec) of IC50 of 0.38 μM, 1.1 μM, and 2.3 μM, respectively.
-
DescriptionDyngo-49 is a dynamin inhibitor.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoAnimal Model:CD-1 mice.Dosage:30 mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; 1.5–2 h before BoNT/A injection Result:Protected BoNT/A-induced paralysis in vivo.
-
SynonymsDyngo-49 | Dyngo 49 | Hydroxy Dynasore
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorDynI (brain)| DynI (rec)| DynII (rec)
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1256493-34-1
-
Formula Weight338.31
-
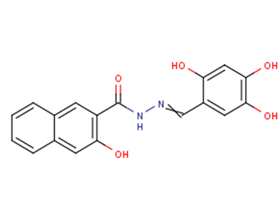
Molecular FormulaC18H14N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (147.79 mM)
-
SMILESc1c(c(cc2ccccc12)O)C(=O)NN=Cc1c(cc(c(c1)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name3-Hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylic acid 2-[(2,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Harper CB., Targeting membrane trafficking in infection prophylaxis: dynamin inhibitors. Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;23(2):90-101.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tangshenoside I
Tangshenoside I might be a potential bioactive marker related to the hematopoietic and immunologic functions of Codonopsis Radix, which could be recommended as the index compound. It has α-glucosidase inhibition activity.
-
[Pro3]-GIP (Rat)
High affinity rat GIP receptor partial agonist (Kd = 13 nM). Increases cAMP accumulation in COS-7 cells transfected with rat GIP receptor, while also acting as a competitive antagonist of GIP.
-
Rozanolixizumab
Rozanolixizumab (RYSTIGGO) is a high-affinity humanized immunoglobulin G4 monoclonal antibody targeting Fc receptors (FcRn) in human newborns for the study of pathogenic IgG in autoimmune and alloimmune diseases.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


