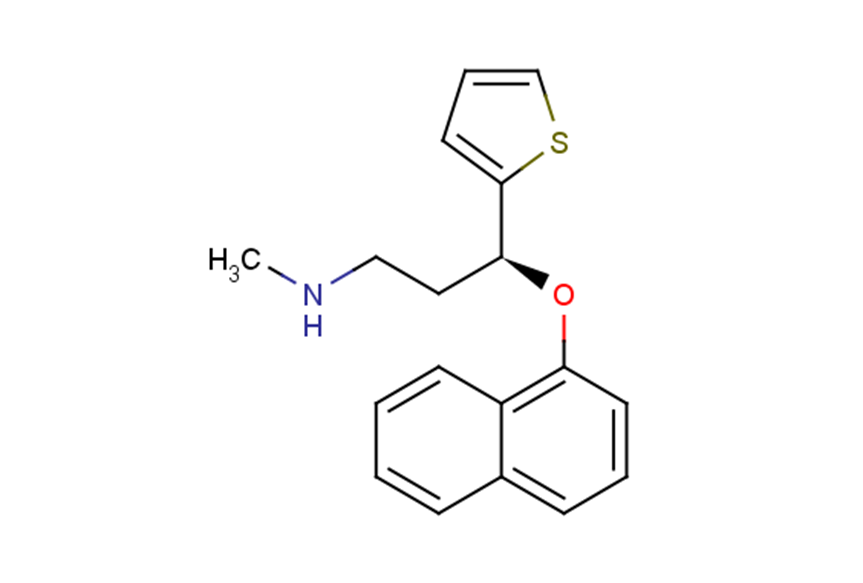
Duloxetine
CAS No. 116539-59-4
Duloxetine( —— )
Catalog No. M21972 CAS No. 116539-59-4
Duloxetine is an inhibitor of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake(Ki of 4.6 nM),with treatment of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 85 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDuloxetine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDuloxetine is an inhibitor of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake(Ki of 4.6 nM),with treatment of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.
-
DescriptionDuloxetine is an inhibitor of serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake(Ki of 4.6 nM),with treatment of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.IC50 of duloxetine for the resting and inactivated wild-type hNav1.7 Na+ channel were 22.1+/-0.4 and 1.79+/-0.10 microM, respectively (mean+/-SE, n=5).?The IC50 for the open Na+ channel was 0.25+/-0.02 microM (n=5), as determined by the block of persistent late Nav1.7 Na+ currents.?Similar open-channel block by duloxetine was found in the muscle Nav1.4 isoform (IC50=0.51+/-0.05 microM;?n=5).?Block by duloxetine appeared via the conserved local anesthetic receptor as determined by site-directed mutagenesis.?Finally, duloxetine elicited strong use-dependent block of neuronal transient Nav1.7 Na+ currents during repetitive stimulations.
-
In VitroDuloxetine ((S)-Duloxetine) inhibits the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system. Duloxetine is also considered a less potent inhibitor of dopamine reuptake. However, duloxetine has no significant affinity for dopaminergic, adrenergic, cholinergic, histaminergic, opioid, glutamate, and GABA receptors and can therefore be considered to be a selective reuptake inhibitor at the 5-HT and NA transporters. Duloxetine undergoes extensive metabolism, but the major circulating metabolites do not contribute significantly to the pharmacologic activity. Major depressive disorder is believed to be due in part to an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system. Antidepressants including ones with a similar mechanism of action as duloxetine, i.e. serotonin metabolism inhibition, cause a decrease in proinflammatory cytokine activity and an increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines; this mechanism may apply to duloxetine in its effect on depression but research on cytokines specific to duloxetine therapy is lacking. The analgesic properties of duloxetine in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy and central pain syndromes such as fibromyalgia are believed to be due to sodium ion channel blockade.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorserotonin-norepinephrine reuptake
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number116539-59-4
-
Formula Weight297.42
-
Molecular FormulaC18H19NOS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCNCC[C@H](Oc1cccc2ccccc12)c1cccs1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Wang, S.Y., J. Calderon, and G. Kuo Wang, Block of neuronal Na+ channels by antidepressant duloxetine in a state-dependent manner. Anesthesiology, 2010. 113(3): p. 655-65.2. Ekram, A, R,et al. Duloxetine in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review[J]. Clinical Journal of Pain, 2016.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Propargyl-PEG5-Ms
Propargyl-PEG5-Ms is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
RXFP3/4 agonist 2
RXFP3/4 agonist 2 is a potent, non-peptidic bis-RXFP3/4 agonist that facilitates the interaction between RXFP3 and β-arrestin-2 and is useful for studying diseases caused by metabolic abnormalities.
-
Mirificin
Puerarin has been investigated for the treatment of Alcohol Abuse.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


