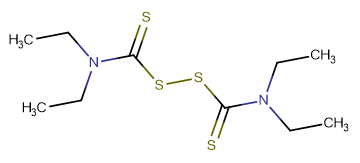
Disulfiram
CAS No. 97-77-8
Disulfiram( NSC 25953 | Tetraethylthiuram disulfide )
Catalog No. M16885 CAS No. 97-77-8
Disulfiram is a specific inhibitor of aldehyde-dehydrogenase (ALDH1), used for the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDisulfiram
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDisulfiram is a specific inhibitor of aldehyde-dehydrogenase (ALDH1), used for the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol.
-
DescriptionDisulfiram is a specific inhibitor of aldehyde-dehydrogenase (ALDH1), used for the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol.(In Vitro):Disulfiram-copper complex potently inhibits the proteasomal activity in cultured breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MCF10DCIS.com cells, but not normal, immortalized MCF-10A cells, before induction of apoptotic cancer cell death. Disulfiram (DS), a clinically used anti-alcoholism drug, strongly inhibits constitutive and 5-FU-induced NF-kappaB activity in a dose-dependent manner. Disulfiram inhibits both NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity but has no effect on 5-FU-induced IkappaBalpha degradation. Disulfiram significantly enhances the apoptotic effect of 5-FU on DLD-1 and RKO(WT) cell lines and synergistically potentiated the cytotoxicity of 5-FU to both cell lines. Disulfiram also effectively abolishes 5-FU chemoresistance in a 5-FU resistant cell line H630(5-FU) in vitro. Oseltamivir decreases the number of viable cells, and the addition of CuCl2 significantly enhances the DSF-induced cell death to less than 10% of control. Disulfiram given to melanoma cells in combination with Cu2+ or Zn2+ decreases expression of cyclin A and reduces proliferation in vitro at lower concentrations than disulfiram alone.Disulfiram (0.1 nM-10 μM; 72 h)?+?Cu2+ combination enhances the cytotoxicity on ovarian cancer cell lines. (In Vivo):Disulfiram significantly inhibits the tumor growth (by 74%), associated with in vivo proteasome inhibition (as measured by decreased levels of tumor tissue proteasome activity and accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and natural proteasome substrates p27 and Bax) and apoptosis induction (as shown by caspase activation and apoptotic nuclei formation) in mice bearing MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts. Disulfiram blocks the P-glycoprotein extrusion pump, inhibits the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB, sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy, reduces angiogenesis, and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Disulfiram inhibits growth and angiogenesis in melanomas transplanted in severe combined immunodeficient mice, and these effects are potentiated by Zn2+ supplementation.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNSC 25953 | Tetraethylthiuram disulfide
-
PathwayMetabolic Enzyme/Protease
-
TargetDehydrogenase
-
RecptorALDH1| DBH
-
Research AreaMetabolic Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number97-77-8
-
Formula Weight296.54
-
Molecular FormulaC10H20N2S4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 59 mg/mL (198.96 mM); DMSO: 59 mg/mL (198.96 mM)
-
SMILESS=C(SSC(N(CC)CC)=S)N(CC)CC
-
Chemical NameBis(diethylthiocarbamyl) disulfide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mackenzie IS, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Sep; 25(9):1891-5.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Diammonium Glycyrrhi...
Diammonium glycyrrhizinate is a widely used anti-inflammatory agent isolated from the licorice root.
-
Epostane
Epostane acts as an antiprogestogen and terminates pregnancy by inhibiting 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and preventing the biosynthesis of progesterone and pregnenolone.
-
Bavachinin
Bavachinin(7-O-Methylbavachin) is a natural compound isolated from the Chinese herb Fructus Psoraleae with potent anti-angiogenic activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


