Dihydroethidium
CAS No. 104821-25-2
Dihydroethidium( Hydroethidine | PD-MY 003 )
Catalog No. M10238 CAS No. 104821-25-2
Dihydroethidium(Hydroethidine; PD-MY 003) is a superoxide indicator.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 47 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 77 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 165 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 246 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 419 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydroethidium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydroethidium(Hydroethidine; PD-MY 003) is a superoxide indicator.
-
DescriptionDihydroethidium(Hydroethidine; PD-MY 003) is a superoxide indicator; exhibits blue-fluorescence in the cytosol until oxidized, where it intercalates within the cell's DNA, staining its nucleus a bright fluorescent red.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsHydroethidine | PD-MY 003
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number104821-25-2
-
Formula Weight315.41
-
Molecular FormulaC21H21N3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
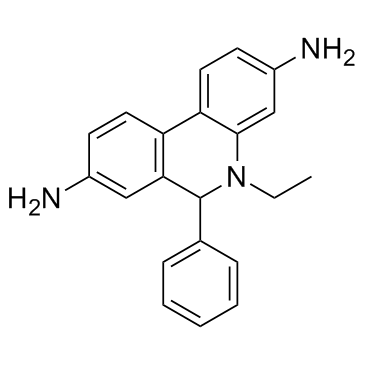
SMILESNC1=CC=C2C3=C(C=C(N)C=C3)C(C4=CC=CC=C4)N(CC)C2=C1
-
Chemical Name5-ethyl-5,6-dihydro-6-phenyl-3,8-phenanthridinediamine
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Zielonka J, et al. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 27;287(5):2984-95.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Didemnin B
Didemnin B is a cyclic depsipeptide that has antiviral and antitumor activity.
-
NSC45586
NSC45586 is a protein phosphatase PHLPP inhibitor, which is selective for PHLPP1 and PHLPP2.
-
Hepcidin antagonist-...
Hepcidin antagonist-1 is an iron-modulating antagonist.Hepcidin antagonist-1 can be used to study metabolic disorders such as iron-deficiency diseases and anemia.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


