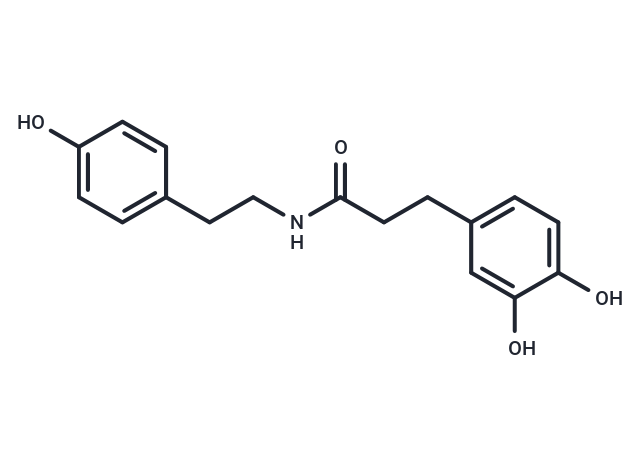
Dihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine
CAS No. 501939-19-1
Dihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine( —— )
Catalog No. M37865 CAS No. 501939-19-1
Dihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine is a compound extracted from Lycii Cortex that has antioxidant and antifungal activities and can be used to study fungal infections.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 217 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 339 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 505 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 789 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1086 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1431 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine is a compound extracted from Lycii Cortex that has antioxidant and antifungal activities and can be used to study fungal infections.
-
DescriptionDihydro-N-Caffeoyltyramine is a compound extracted from Lycii Cortex that has antioxidant and antifungal activities and can be used to study fungal infections.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetAntioxidant
-
RecptorAntioxidant | Antifungal
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number501939-19-1
-
Formula Weight301.34
-
Molecular FormulaC17H19NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(NCCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1)CCC2=CC=C(O)C(O)=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Isoscoparin
Isoscoparin is derived from Gentiana algida Pall with antioxidant and anti-adipogenic activities. Isoscoparin can be used in stuides about the prevention and treatment of obesity.
-
KukoaMine B
Kukoamine B is a component of Lycii Cortex with anti-oxidant anti-acute inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties.
-
Cinnamtannin B-1
Cinnamtannin B1 is an A-type proanthocyanidin contained in several plant species such as Vaccinium vitis-idaea, Laurus nobilis L., Cinnamomum zeylanicum, and Lindera umbellata.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


