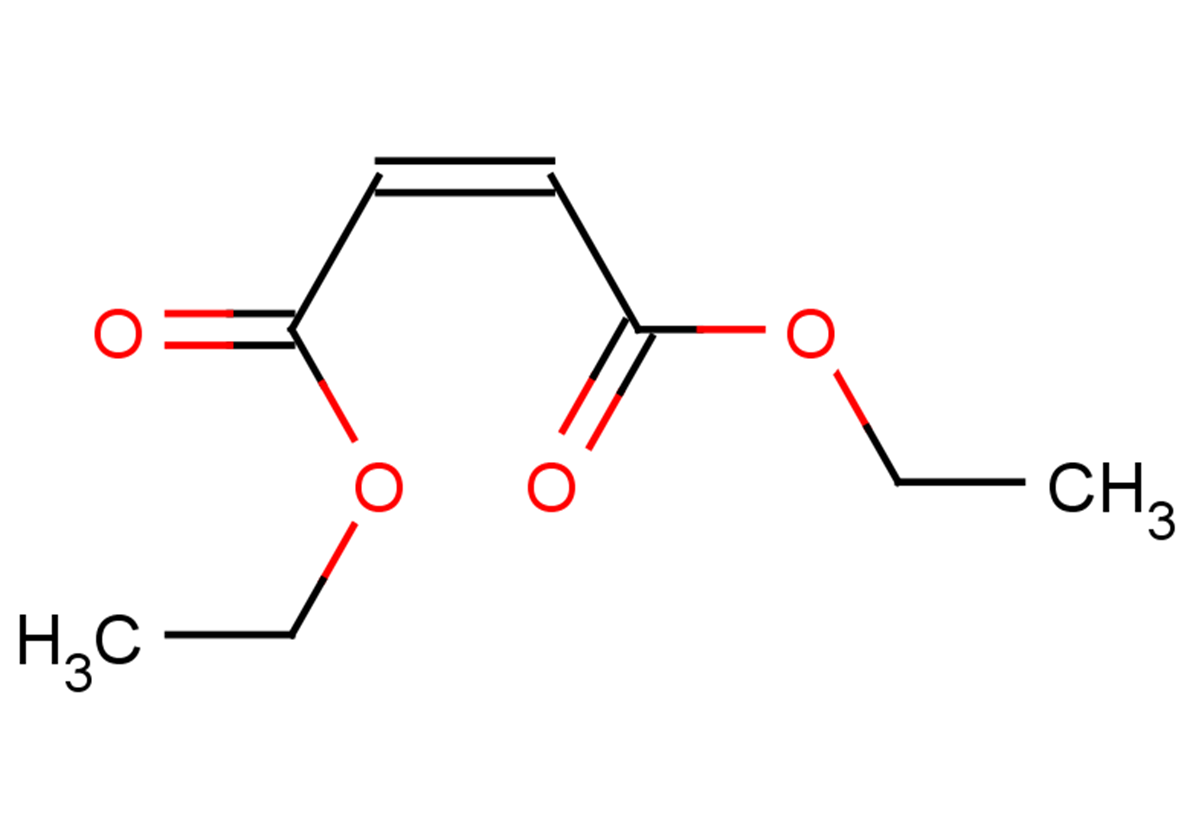
Diethylmaleate
CAS No. 141-05-9
Diethylmaleate( DIETHYL MALEATE | Maleic acid, diethyl ester | Diethylmaleate )
Catalog No. M23567 CAS No. 141-05-9
Diethylmaleate is the diethyl ester of maleic acid and a glutathione-depleting compound that inhibits NF-kB.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 112 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDiethylmaleate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDiethylmaleate is the diethyl ester of maleic acid and a glutathione-depleting compound that inhibits NF-kB.
-
DescriptionDiethylmaleate is the diethyl ester of maleic acid and a glutathione-depleting compound that inhibits NF-kB.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDIETHYL MALEATE | Maleic acid, diethyl ester | Diethylmaleate
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetNF-κB
-
RecptorNF-κB
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number141-05-9
-
Formula Weight172.18
-
Molecular FormulaC8H12O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?Ethanol : ≥ 100 mg/mL (580.79)
-
SMILESO=C(OCC)/C=C\C(OCC)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Wedelolactone
Wedelolactone inhibits adipogenic differentiation through ERK pathway, may be a novel inhibitory effect on adipogenic differentiation in hAMSCs.
-
Scandoside
Scandoside, a cyclic enolide that can be isolated from Haemophilus difficile, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity, inhibits the expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), TNF-α, and IL-6 messenger RNA (mRNA), and inhibits the nuclear transcription factor, kappa-B alpaha (IκB-α), p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor phosphorylation.
-
SR12343
SR12343 (SR-12343) is a novel NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO)-binding domain (NBD) mimetic for inhibiting IKK/NF-κB activation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


