DHBS
CAS No. 54970-72-8
DHBS( DCHBS )
Catalog No. M24537 CAS No. 54970-72-8
DHBS is used in conjunction with 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) and H2O2 for chromogenic quantitation of peroxidase in coupled enzymatic reactions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1G | 43 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDHBS
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDHBS is used in conjunction with 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) and H2O2 for chromogenic quantitation of peroxidase in coupled enzymatic reactions.
-
DescriptionDHBS is used in conjunction with 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) and H2O2 for chromogenic quantitation of peroxidase in coupled enzymatic reactions.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDCHBS
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number54970-72-8
-
Formula Weight265.05
-
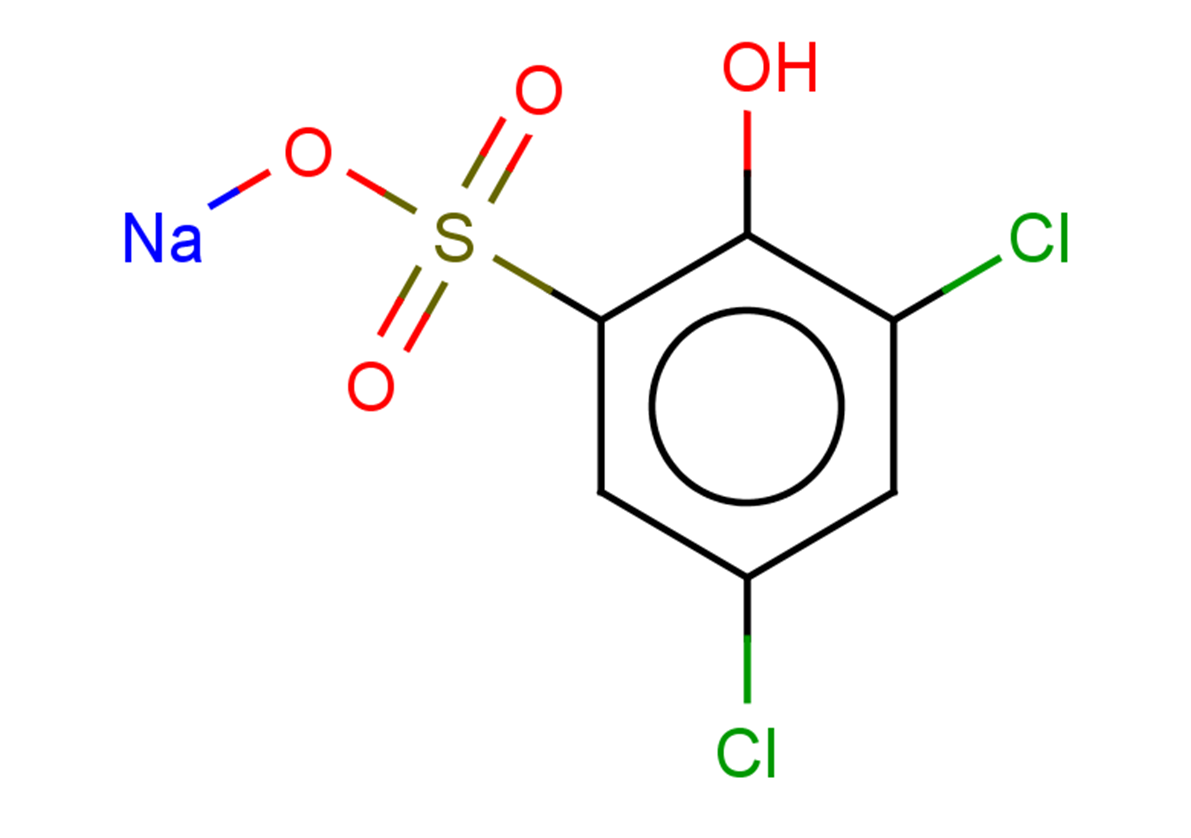
Molecular FormulaC6H3Cl2NaO4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:30 mg/mL (113.18 mM)
-
SMILESOc1c(Cl)cc(Cl)cc1S(=O)(=O)O[Na]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Azido-PEG4-azide
Azido-PEG4-azide is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used to synthesize PROTACs.
-
Monobutyl Phthalate
Used in organic synthesis, medicine industry.
-
Methyl cyclohexaneca...
Methyl cyclohexanecarboxylate is an endogenous metabolite and used as a material for chemical synthesis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


