DCB
CAS No. 6971-97-7
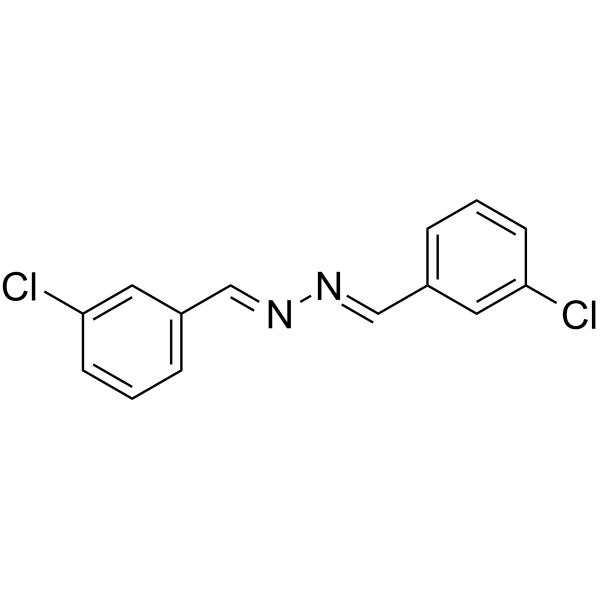
DCB( 3,3'-dichlorobenzaldazine )
Catalog No. M27621 CAS No. 6971-97-7
DCB is an allosteric ligand for mGluR5 and shows the negative modulatory effect of 3,3′-dimethoxybenzaldazine (DMeOB).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 50 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 68 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 160 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 267 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 430 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 945 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDCB
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDCB is an allosteric ligand for mGluR5 and shows the negative modulatory effect of 3,3′-dimethoxybenzaldazine (DMeOB).
-
DescriptionDCB is an allosteric ligand for mGluR5 and shows the negative modulatory effect of 3,3′-dimethoxybenzaldazine (DMeOB). DCB blocks the positive allosteric regulation of mGluRs with the help of 3,3′-difluorobenzaldazine (DFB).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms3,3'-dichlorobenzaldazine
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorBacterial
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6971-97-7
-
Formula Weight277.15
-
Molecular FormulaC14H10Cl2N2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (90.20 mM)
-
SMILESClc1cccc(\C=N\N=C/c2cccc(Cl)c2)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Paganelli FL, et al. Lipoteichoic acid synthesis inhibition in combination with antibiotics abrogates growth of multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium.Int J Antimicrob Agents.?2017?Mar;49(3):355-363.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Alkynyl myristic aci...
Alkynyl myristic acid is an alkyl chain-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
Compound 1T-0216
Compound 1T-0216 is a chemical compound.
-
Ginsenoside Rg1
Ginsenosides are a class of steroid glycosides, and triterpene saponins found exclusively in the plant genus Panax (ginseng).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


