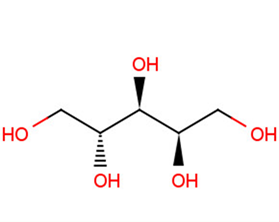
D-Arabitol
CAS No. 488-82-4
D-Arabitol( D-Lyxitol )
Catalog No. M20045 CAS No. 488-82-4
D-Arabitol is a polyol. Polyols are sugar alcohols linked to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Polyols occur in body fluids. It is thought that D-arabitol is a metabolic end-product in humans.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD-Arabitol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD-Arabitol is a polyol. Polyols are sugar alcohols linked to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Polyols occur in body fluids. It is thought that D-arabitol is a metabolic end-product in humans.
-
DescriptionD-Arabitol is a polyol. Polyols are sugar alcohols linked to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Polyols occur in body fluids. It is thought that D-arabitol is a metabolic end-product in humans.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsD-Lyxitol
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number488-82-4
-
Formula Weight152.15
-
Molecular FormulaC5H12O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:197.2 mM
-
SMILESOC[C@@H](O)C(O)[C@H](O)CO
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Klusmann A et al. Influence of D-arabitol and ribitol on neuronal network activity. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(6):1181-3.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Hydroxyisogermafuren...
Hydroxyisogermafurenolide is a natural prodrct from Curcumae Radix.
-
Denatonium benzoate
Denatonium is a quaternary ammonium cation. It is a compound of a salt with an inert anion like benzoate or saccharide.
-
Palmitic acid ethyl ...
Used as softener and lubricant.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


