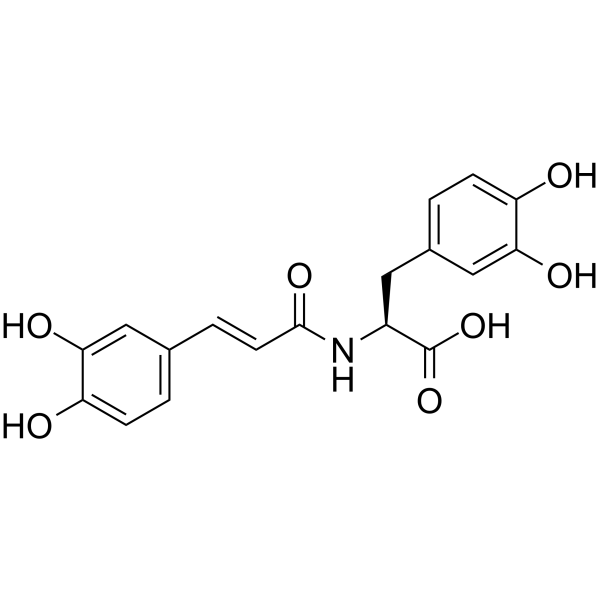
Clovamide
CAS No. 53755-02-5
Clovamide( N-trans-Caffeoy-L-dopa | trans-Clovamide )
Catalog No. M27835 CAS No. 53755-02-5
Trans-Clovamide is a naturally occurring caffeoyl conjugate identified in the antioxidant polyphenolic fraction of cocoa (T. cacao L.) Trans-Clovamide is a potent antioxidantand that has shown neuroprotective effects (EC50s = 0.9-3.7 μM) in several in vitro models of neuronal death.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 31 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 50 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 80 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 125 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 222 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 380 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameClovamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTrans-Clovamide is a naturally occurring caffeoyl conjugate identified in the antioxidant polyphenolic fraction of cocoa (T. cacao L.) Trans-Clovamide is a potent antioxidantand that has shown neuroprotective effects (EC50s = 0.9-3.7 μM) in several in vitro models of neuronal death.
-
DescriptionTrans-Clovamide is a naturally occurring caffeoyl conjugate identified in the antioxidant polyphenolic fraction of cocoa (T. cacao L.) Trans-Clovamide is a potent antioxidantand that has shown neuroprotective effects (EC50s = 0.9-3.7 μM) in several in vitro models of neuronal death. Trans-Clovamide is an excellent ROS and oxygen radical scavenger and also has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Clovamide is an anti-microbial with activity against the human pathogens influenza A subtype H5N1, Trypanosoma evansi, and Heliobacter pylori.(In Vitro):Clovamide protects neurons from injury in three in vitro models of neuronal death: oxidative stress, excitotoxicity and OGD/reoxygenation. In SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, Clovamide (10-100 μM) protects cell death significantly with an EC50 value of 3.6 μM. Clovamide inhibits growth of three pathogens of cacao in the genus?Phytophthora, is a substrate for cacao polyphenol oxidase, and is a contributor to enzymatic browning. Clovamide inhibits proteinase and pectinase in vitro. Clovamide also enhances PPARγ expression.
-
In VitroClovamide is able to protect neurons from injury in three in vitro models of neuronal death: oxidative stress, excitotoxicity and OGD/reoxygenation. In SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, Clovamide (10-100 μM) significantly protects cell death, with an EC50 value of 3.6 μM. Clovamide also significantly enhances PPARγ expression.Clovamide inhibits growth of three pathogens of cacao in the genus Phytophthora, is a substrate for cacao polyphenol oxidase, and is a contributor to enzymatic browning. Clovamide inhibiteds proteinase and pectinase in vitro.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsN-trans-Caffeoy-L-dopa | trans-Clovamide
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number53755-02-5
-
Formula Weight359.334
-
Molecular FormulaC18H17NO7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (347.87 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)[C@H](Cc1ccc(O)c(O)c1)NC(=O)\C=C\c1ccc(O)c(O)c1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Nilasha Banerjee, et al. Estrone-3-sulphate, a potential novel ligand for targeting breast cancers. PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e64069.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pyrazoloacridine
Pyrazoloacridine is a nucleic acid binding agent that inhibits the activity of topo I and II with an IC50 of 1.25 μM in K562 cells. Pyrazoloacridine shows anti-cancer activity.
-
CCT128930 hydrochlor...
CCT128930 hydrochloride is a potent and selective inhibitor of AKT with IC50 of 6 nM. CCT128930 hydrochloride induces cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, and autophagy.
-
Curzerene
Curzerene is a sesquiterpene is isolated from the rhizome of Curculigo orchioides Gaertn with anti-cancer activity. Curzerene induces cell apoptosis[1].Curzerene inhibits glutathione S-transferase A1 (GSTA1) mRNA and protein expression.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


