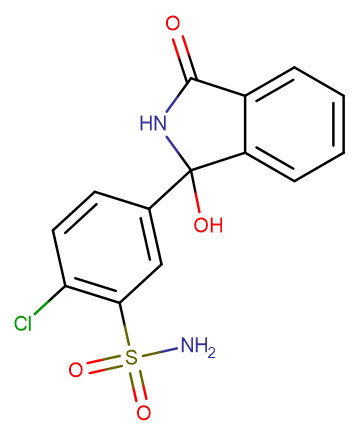
Chlortalidone
CAS No. 77-36-1
Chlortalidone( Hygroton | NSC 69200 | Oradil | Thalitone )
Catalog No. M15922 CAS No. 77-36-1
Chlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic used to treat hypertension.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 59 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 142 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameChlortalidone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionChlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic used to treat hypertension.
-
DescriptionChlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic used to treat hypertension.(In Vivo):Chlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic. After oral intake, peak serum concentrations are achieved in 2-6 hours. The half-life of Chlorthalidone is approximately 42 (range 29-55) hours, reaching 45-60 hours after long-term dosing. However, interindividual variability in the half-life of Chlorthalidone is wide. Chlorthalidone is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The natriuretic effect of Chlorthalidone is maximal at 18 hours and lasts more than 48 hours. Comparing different doses of Chlorthalidone, it has been observed that 25 mg daily is nearly as effective as higher doses, but with less risk of hypokalemia. Chlorthalidone reduces calcium oxalate calculous recurrence but magnesium hydroxide does not. The effectiveness of Chlorthalidone or magnesium hydroxide is examined in the prevention of recurrent calcium oxalate kidney calculi. In a double-blind random allocation design daily dosages of 25 or 50 mg. Chlorthalidone, 650 or 1,300 mg. magnesium hydroxide, or an identical placebo are administered. All groups showed significantly decreased calculous events compared to the pretreatment rates. During the trial 56.1 per cent fewer calculi than predicted developed in the placebo group (p less than 0.01), whereas the groups receiving low and high dosage magnesium hydroxide showed 73.9 and 62.3 per cent fewer calculi, respectively (p less than 0.001 and less than 0.01, respectively). Chlorthalidone treatment results in a 90.1 per cent decrease from predicted rates and both dosages yielded similar results. When the treatments are compared Chlorthalidone is significantly better than the placebo or magnesium hydroxide (p less than 0.01). The large decreases in calculous events seen when placebo or ineffective therapy is given underscore the positive treatment bias that occurs when historical controls are used and they demonstrate the need for proper experimental design.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoChlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic. After oral intake, peak serum concentrations are achieved in 2-6 hours. The half-life of Chlorthalidone is approximately 42 (range 29-55) hours, reaching 45-60 hours after long-term dosing. However, interindividual variability in the half-life of Chlorthalidone is wide. Chlorthalidone is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The natriuretic effect of Chlorthalidone is maximal at 18 hours and lasts more than 48 hours. Comparing different doses of Chlorthalidone, it has been observed that 25 mg daily is nearly as effective as higher doses, but with less risk of hypokalemia. Chlorthalidone reduces calcium oxalate calculous recurrence but magnesium hydroxide does not. The effectiveness of Chlorthalidone or magnesium hydroxide is examined in the prevention of recurrent calcium oxalate kidney calculi. In a double-blind random allocation design daily dosages of 25 or 50 mg. Chlorthalidone, 650 or 1,300 mg. magnesium hydroxide, or an identical placebo are administered. All groups showed significantly decreased calculous events compared to the pretreatment rates. During the trial 56.1 per cent fewer calculi than predicted developed in the placebo group (p less than 0.01), whereas the groups receiving low and high dosage magnesium hydroxide showed 73.9 and 62.3 per cent fewer calculi, respectively (p less than 0.001 and less than 0.01, respectively). Chlorthalidone treatment results in a 90.1 per cent decrease from predicted rates and both dosages yielded similar results. When the treatments are compared Chlorthalidone is significantly better than the placebo or magnesium hydroxide (p less than 0.01). The large decreases in calculous events seen when placebo or ineffective therapy is given underscore the positive treatment bias that occurs when historical controls are used and they demonstrate the need for proper experimental design.
-
SynonymsHygroton | NSC 69200 | Oradil | Thalitone
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorNa+/Ca2+ Exchanger
-
Research AreaCardiovascular Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number77-36-1
-
Formula Weight338.77
-
Molecular FormulaC14H11ClN2O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Water
-
SMILESC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=O)NC2(C3=CC(=C(C=C3)Cl)S(=O)(=O)N)O
-
Chemical Name2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2H-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Baker WL, et al. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2014 Jul;12(7):791-8.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Oxyfluorfen
Oxyfluorfen, a herbicide of the nitrodiphenyl ether class, is used to control annual and perennial broad-leaved weeds and sedges in a variety of field crops.
-
chaetoglobosin Vb
chaetoglobosin Vb is a new cytochalasan alkaloid isolated?from endophytic Chaetomium globosum.
-
Pseudobaptigenin
Pseudobaptigenin (Psi-baptigenin) is an isoflavone, a flavonoid lipid molecule that is a natural product found in Pterocarpus marsupium, Dalbergia spruceana.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


