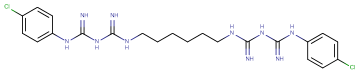
Chlorhexidine
CAS No. 55-56-1
Chlorhexidine( Chlorhexidine | EC 200-238-7 )
Catalog No. M15019 CAS No. 55-56-1
Chlorhexidine is an antibacterial used as an antiseptic and for other applications.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 32 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameChlorhexidine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionChlorhexidine is an antibacterial used as an antiseptic and for other applications.
-
DescriptionChlorhexidine is an antibacterial used as an antiseptic and for other applications. (In Vivo):Chlorhexidine gluconate (ip) reduces postoperative intra-abdominal infection in mice at the end of colon surgery.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoChlorhexidine gluconate (ip) reduces postoperative intra-abdominal infection in mice at the end of colon surgery. Animal Model:One hundred and eighty male Imprinting Control Region (ICR) mice at 6 to8-wk-old (body weight, 25 ± 3 g) were randomized to six groups.Dosage:Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.05%, and Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.025%.Administration:One-time intraperitoneal injection.Result:A total of 48 mice (26.7%) developed postoperative intra-abdominal abscesses. Mice that had Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.05% lavage had significantly lower incidence of postoperative intra-abdominal abscesses compared with that of group D mice that had saline lavage only (P = 0.0113). Microscopic peritoneal fibrosis occurred significantly more among group E mice that had Chlorhexidine gluconate 0.05% lavage compared with group D mice that had saline lavage only (P = < 0.005).
-
SynonymsChlorhexidine | EC 200-238-7
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifection
-
RecptorHNMT| CAT
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number55-56-1
-
Formula Weight505.45
-
Molecular FormulaC22H30Cl2N10
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in DMSO
-
SMILESN=C(NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1)NC(NCCCCCCNC(NC(NC2=CC=C(Cl)C=C2)=N)=N)=N
-
Chemical Name2,4,11,13-Tetraazatetradecanediimidamide, N,N''-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
alpha-Terpineol
Terpineol possesses antifungal activity against Trichophyton mentagrophytes, it also exhibits strong antimicrobial activity against periodontopathic and cariogenic bacteria. α-Terpineol shows anticonvulsant, and anti-inflammatory activities, it inhibits the gene expression of the IL-6 receptor.
-
Licoflavone B
Licoflavone B has schistosomicidal activity, it showed high S. mansoni ATPase (IC50 of 23.78 μM) and ADPase (IC50 of 31.50 μM) inhibitory activities.
-
Fuziline
Fuziline shows significant insecticidal activity against Nilaparvata legen and Aphis medicagini. Fuziline shows activity against pentobarbital sodiuminduced cardiomyocytes damage by obviously recovering beating rhythm and increasing the cell viability.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


