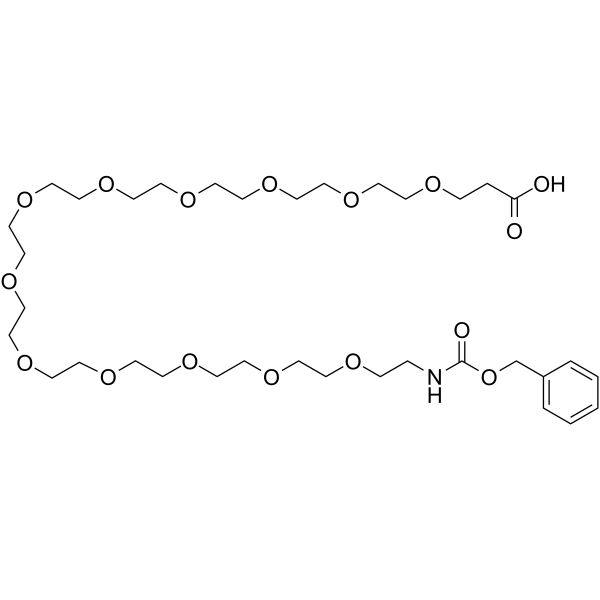
Cbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid
CAS No. 1334177-88-6
Cbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid( —— )
Catalog No. M26935 CAS No. 1334177-88-6
Cbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTAC.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 48 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 68 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 107 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 158 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 233 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 332 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTAC.
-
DescriptionCbz-NH-PEG12-C2-acid is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTAC.
-
In VitroPROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAMPK| Glucokinase| PPARα
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1334177-88-6
-
Formula Weight751.864
-
Molecular FormulaC35H61NO16
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOC(=O)CCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCNC(=O)OCc1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Yang ZH, et al. Chronic administration of palmitoleic acid reduces insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation in KK-Ay Mice with genetic type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Jul 21;10:120.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-Bromopyruvic acid
3-Bromopyruvic acid is a hexokinase II inhibitor with Ki of 2.4 mM for glycolysis/hexokinase inhibition. It is inhibitor of tumour cell energy metabolism and chemopotentiator of platinum drugs.
-
Murrayone
Murrayone, a coumarin-containing compound extracted from M. paniculata, is the most bioactive substance in this species and is a cancer metastasis chemopreventive agent based on its unique pharmacological properties.
-
Prepro-Neuromedin S ...
Prepro-Neuromedin S (70-103) (human)



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


