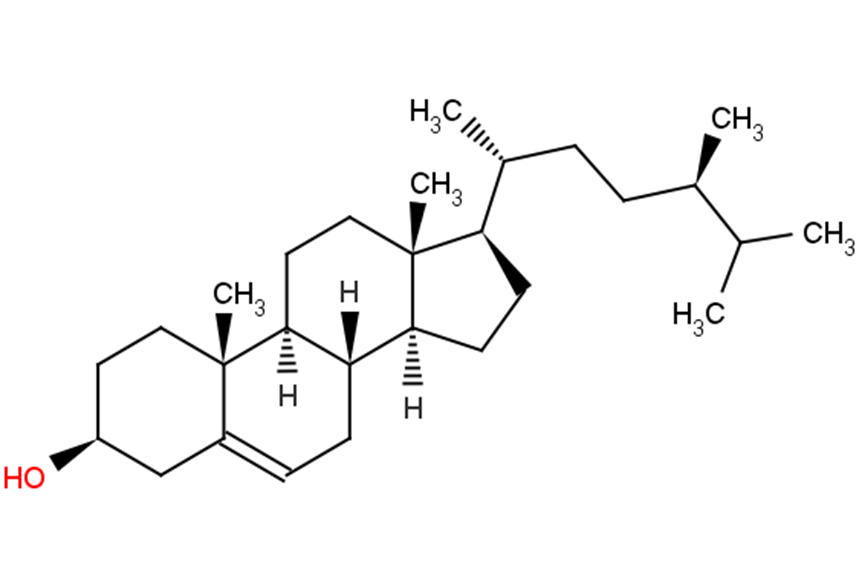
Campesterol
CAS No. 474-62-4
Campesterol( (24R)-5-Ergosten-3β-ol )
Catalog No. M22586 CAS No. 474-62-4
Campesterol is a plant sterol with cholesterol lowering and anticarcinogenic effects, it and other plant sterols often decrease LDL cholesterol levels overall. Campesterol has anti-inflammatory effect, it inhibits several pro-inflammatory and matrix degradation mediators typically involved in osteoarthritis- induced cartilage degradation, also sometimes used to treat some specific prostate conditions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 116 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 176 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 295 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 440 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 642 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCampesterol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCampesterol is a plant sterol with cholesterol lowering and anticarcinogenic effects, it and other plant sterols often decrease LDL cholesterol levels overall. Campesterol has anti-inflammatory effect, it inhibits several pro-inflammatory and matrix degradation mediators typically involved in osteoarthritis- induced cartilage degradation, also sometimes used to treat some specific prostate conditions.
-
DescriptionCampesterol is a plant sterol with cholesterol lowering and anticarcinogenic effects, it and other plant sterols often decrease LDL cholesterol levels overall. Campesterol has anti-inflammatory effect, it inhibits several pro-inflammatory and matrix degradation mediators typically involved in osteoarthritis- induced cartilage degradation, also sometimes used to treat some specific prostate conditions.We present a comparative differential scanning calorimetric study of the effects of the animal sterol cholesterol (Chol) and the plant sterols Campesterol (Camp) and brassicasterol (Bras) on the thermotropic phase behavior of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) bilayers.METHODS AND RESULTS: Camp and Bras differ from Chol in having a C24 methyl group and, additionally for Bras, a C22 trans-double bond. Camp and especially Bras decrease the temperature, cooperativity and enthalpy of the DPPC pretransition more than Chol, although these effects are attenuated at higher sterol levels. This indicates that they destabilize gel-state DPPC bilayers to a greater extent, but are less soluble, than Chol. Not surprisingly, all three sterols have similar effects on the sterol-poor sharp component of the DPPC main phase transition. However, Camp and especially Bras less effectively increase the temperature and decrease the cooperativity and enthalpy of the broad component of the main transition than Chol. This indicates that at higher sterol concentrations, Camp and Bras are less miscible and less effective than Chol at ordering the hydrocarbon chains of the sterol-enriched fluid DPPC bilayers. CONCLUSIONS:Overall, these alkyl side chain modifications generally reduce the ability of Chol to produce its characteristic effects on DPPC bilayer physical properties. These differences are likely due to the less extended and more bent conformations of the alkyl side chains of Camp and Bras, producing sterols with a greater effective cross-sectional area and reduced length than Chol. Hence, the structure of Chol is likely optimized for maximum solubility in, as opposed to maximum ordering of, phospholipid bilayers.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(24R)-5-Ergosten-3β-ol
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number474-62-4
-
Formula Weight400.7
-
Molecular FormulaC28H48O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[H][C@@]12CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CC[C@@H](C)C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@]1([H])[C@@]2([H])CC=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]12C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.A comparative calorimetric study of the effects of cholesterol and the plant sterols campesterol and brassicasterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1838(7):1941-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone
1,3-Dihydroxyacetone is the main active ingredient in sunscreen tanning skin care preparations, an important precursor for the synthesis of a variety of fine chemicals, and a food additive that can be produced on an industrial scale by microbial fermentation on Gluconobacter oxydans.
-
DL-Normetanephrine h...
rac-Normetanephrine Hydrochloride is a metabolite of Epinephrine. It is found together with Metanephrine in urine and in certain tissues.
-
CMP-Sialic acid sodi...
CMP-Sialic acid sodium salt (CMP-Neu5Ac sodium salt) is a variant inhibitor of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase, the activated form of sialic acid, which is widely found in animals and is involved in the metabolism of organisms.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


