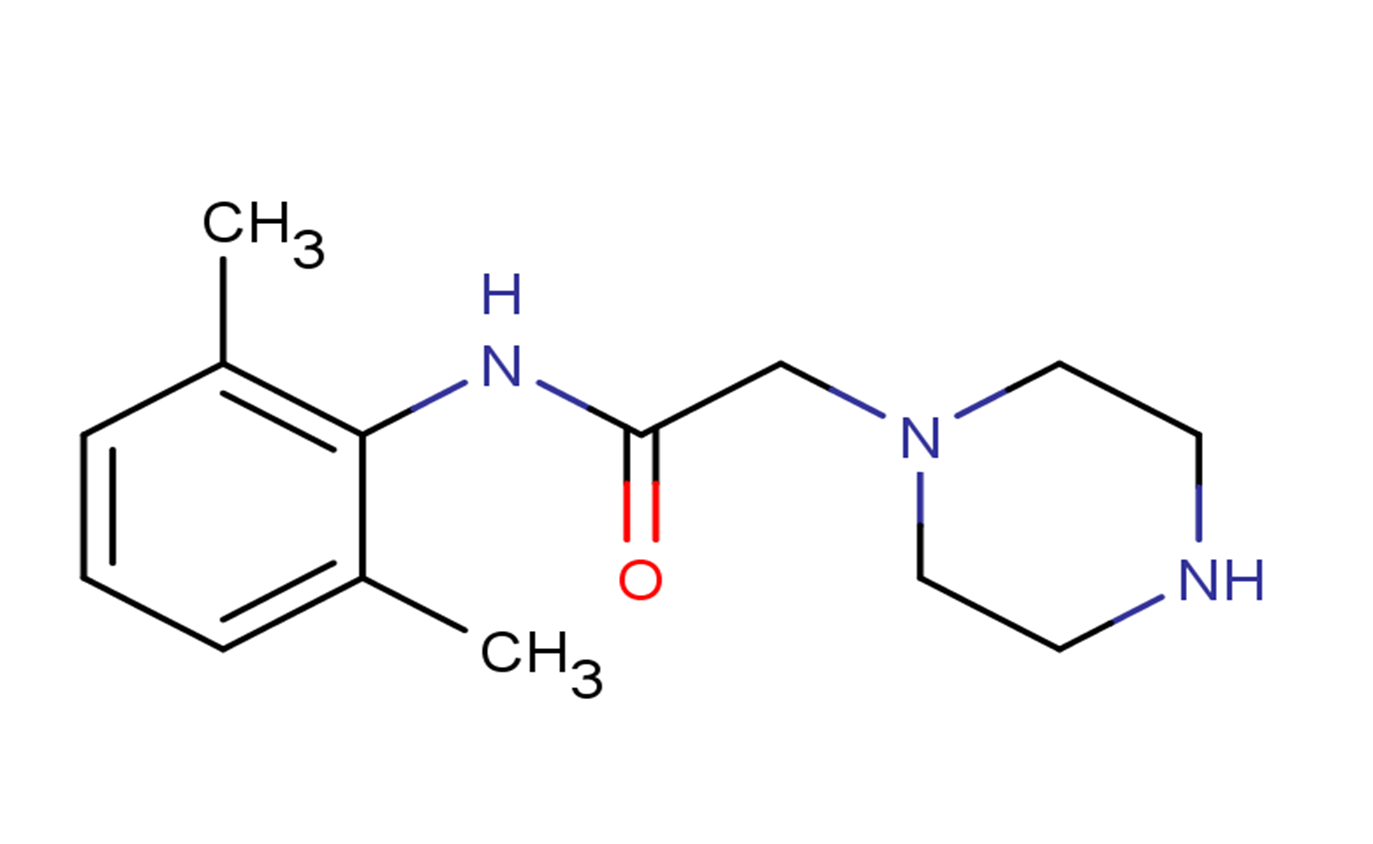
CVT-2738
CAS No. 5294-61-1
CVT-2738( CVT 2738 | CVT2738 | RS-94287 | EC 610-916-8 | UNII-NYS3I6283H )
Catalog No. M24503 CAS No. 5294-61-1
CVT-2738 is a metabolite of Ranolazine. Ranolazine is a partial fatty acid oxidation (pFOX) inhibitor and anti-anginal drug.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 115 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 173 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 258 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 388 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 642 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCVT-2738
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCVT-2738 is a metabolite of Ranolazine. Ranolazine is a partial fatty acid oxidation (pFOX) inhibitor and anti-anginal drug.
-
DescriptionCVT-2738 is a metabolite of Ranolazine. Ranolazine is a partial fatty acid oxidation (pFOX) inhibitor and anti-anginal drug.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsCVT 2738 | CVT2738 | RS-94287 | EC 610-916-8 | UNII-NYS3I6283H
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptorfatty acid oxidation (pFOX)
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5294-61-1
-
Formula Weight247.34
-
Molecular FormulaC14H21N3O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Soluble; Water:Insoluble
-
SMILESCC1=C(C(=CC=C1)C)NC(=O)CN2CCNCC2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Yao Z, Gong S, Guan T, Li Y, Wu X, Sun H. Synthesis of ranolazine metabolites and their anti-myocardial ischemia activities. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Nov;57(11):1218-22. PubMed PMID: 19881270.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2,3-Pentanedione
2,3-Pentanedione is a food additive that also occurs naturally as a fermentation product in beer, wine and yogurt and is released during the roasting of coffee beans.
-
Fargesol
(-)-Fargesol is a nartural product from the flowers buds of Magnolia fargesii,the dried flower buds of M. fargesii, has been used as therapy for nasal empyema and headache.
-
Amino-PEG12-alcohol
Amino-PEG12-alcohol is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


