COX-2-IN-1
CAS No. 787623-48-7
COX-2-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M26018 CAS No. 787623-48-7
COX-2-IN-1 is a potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor (IC50: 3.9 μM).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 264 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 402 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 593 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 888 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1242 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1701 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 3411 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCOX-2-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCOX-2-IN-1 is a potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor (IC50: 3.9 μM).
-
DescriptionCOX-2-IN-1 is a potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor (IC50: 3.9 μM).(In Vitro):COX-2-IN-1(compound 5f) is an inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2 with IC50s of >100 and 3.9 μM, respectively.
-
In VitroCOX-2-IN-1(compound5f) is an inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2 withIC50sof>100 and 3.9 μM, respctively. Comparison of 5b and COX-2-IN-1 shows that smaller halogen atom at 5th position on the indole ring enhances COX-2 enzyme inhibition activity, whereas the presence of a larger bromine atom at 6th position of the ring improves the inhibitory activity (5d, 5e and 5h) of the compound.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetCOX
-
RecptorAlkyl-Chain
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number787623-48-7
-
Formula Weight442.84
-
Molecular FormulaC18H14ClF3N4O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
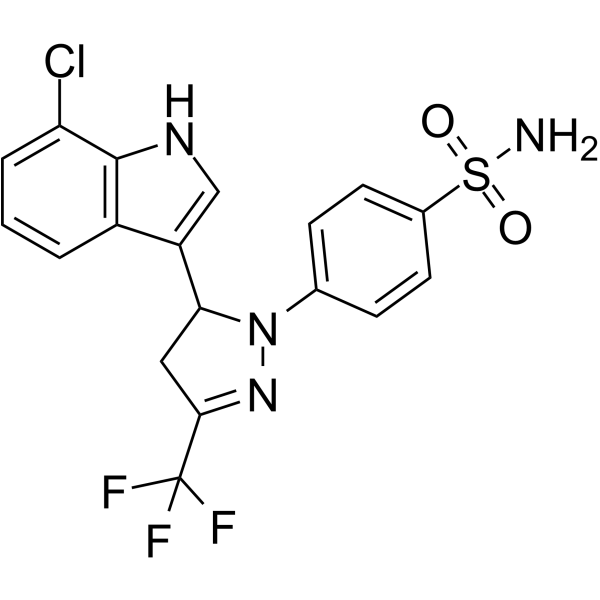
SMILESNS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(cc1)N1N=C(CC1c1c[nH]c2c(Cl)cccc12)C(F)(F)F
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Yang J, et al. Simple Structural Modifications Converting a Bona fide MDM2 PROTAC Degrader into a Molecular Glue Molecule: A Cautionary Tale in the Design of PROTAC Degraders. J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 21.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Feladilimab
Feladilimab (GSK3359609) is an IgG4 monoclonal antibody that is an ICOS agonist.
-
PTUPB
PTUPB is a novel dual acting COX-2/sEH inhibitor with IC50 of 1.26 uM/0.9 nM.
-
Indomethacin heptyl ...
Indomethacin heptyl ester is a non-selective inhibitor of both COX-1 and COX-2



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


