CMF019
CAS No. 1586787-08-7
CMF019( —— )
Catalog No. M26123 CAS No. 1586787-08-7
CMF019 is a potent agonist of the Apelin receptor (APJ) with G protein bias. CMF019 binds to APJ (pKis: 8.58, 8.49, and 8.71 for the human, rat, and mouse).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 233 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 394 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 642 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 887 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1188 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCMF019
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCMF019 is a potent agonist of the Apelin receptor (APJ) with G protein bias. CMF019 binds to APJ (pKis: 8.58, 8.49, and 8.71 for the human, rat, and mouse).
-
DescriptionCMF019 is a potent agonist of the Apelin receptor (APJ) with G protein bias. CMF019 binds to APJ (pKis: 8.58, 8.49, and 8.71 for the human, rat, and mouse).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1586787-08-7
-
Formula Weight455.62
-
Molecular FormulaC25H33N3O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (109.74 mM)
-
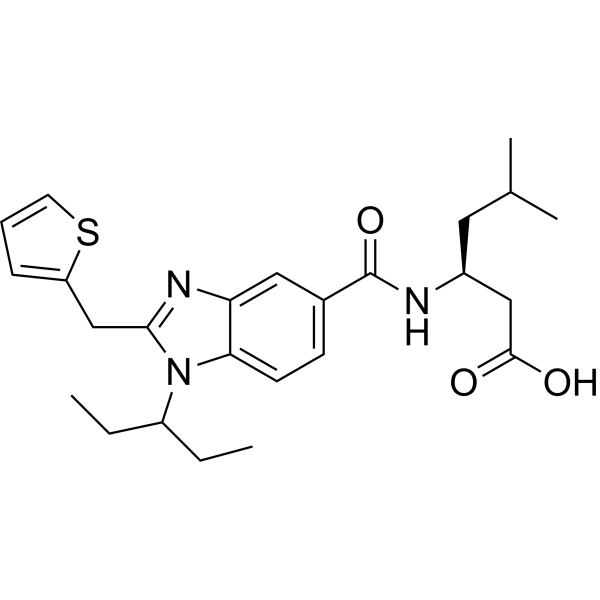
SMILESCCC(CC)n1c(Cc2cccs2)nc2cc(ccc12)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)CC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Paris polyphylla: chemical and biological prospectives. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(6):833-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ganoderic acid C6
Ganoderic acid C6 has antinociceptive activity.
-
N-(3-Aminopropyl)cyc...
N-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexylamine, a cyclohexylamine derivative, acts as a selective and competitive inhibitor of spermidine synthase. N-(3-Aminopropyl)cyclohexylamine can be used for the research of neurological diseases.
-
Substance P b
Substance P b



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


