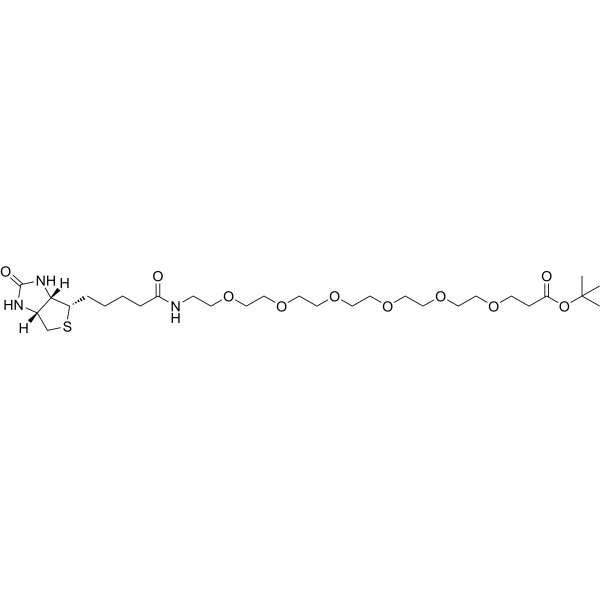
Biotin-PEG6-Boc
CAS No. 1352814-07-3
Biotin-PEG6-Boc( Biotin-PEG6-t-butyl ester )
Catalog No. M26910 CAS No. 1352814-07-3
Biotin-PEG6-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 104 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 152 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 251 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 375 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 556 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1197 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBiotin-PEG6-Boc
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBiotin-PEG6-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
DescriptionBiotin-PEG6-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.(In Vitro):PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In VitroPROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsBiotin-PEG6-t-butyl ester
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorGPR40
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1352814-07-3
-
Formula Weight635.81
-
Molecular FormulaC29H53N3O10S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES[H][C@]12CS[C@@H](CCCCC(=O)NCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)[C@@]1([H])NC(=O)N2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Houze JB, et al. AMG 837: a potent, orally bioavailable GPR40 agonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jan 15;22(2):1267-70.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-epi-Isocucurbitaci...
3-epi-Isocucurbitacin B.
-
Protodioscin
Protodioscin is a major steroidal saponin in dioscoreae rhizome, with anti-hyperlipidemia, anti-cancer properties.
-
3,3-Binaringenin
3',3'''-Binaringenin is a natural product for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


