BILB-1941
CAS No. 494856-61-0
BILB-1941( —— )
Catalog No. M34180 CAS No. 494856-61-0
BILB-1941 (BILB-1941ZW) is an inhibitor of HCV NS5B polymerase and can be used in studies about HCV infection.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 500 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 758 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 1036 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1518 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 2052 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2637 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBILB-1941
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBILB-1941 (BILB-1941ZW) is an inhibitor of HCV NS5B polymerase and can be used in studies about HCV infection.
-
DescriptionBILB 1941 is a potent and specific nonnucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA polymerase in vitro.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorHCV Protease
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number494856-61-0
-
Formula Weight562.66
-
Molecular FormulaC34H34N4O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
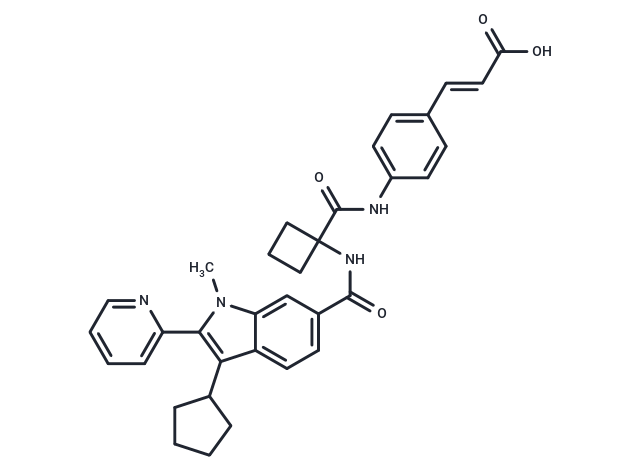
SMILESCN1C(=C(C=2C1=CC(C(NC3(C(NC4=CC=C(/C=C/C(O)=O)C=C4)=O)CCC3)=O)=CC2)C5CCCC5)C6=CC=CC=N6
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Erhardt A, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and antiviral effect of BILB 1941, a novel hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase inhibitor, after 5 days oral treatment. Antivir Ther. 2009;14(1):23-32.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
OV - 2, Sheep
OV - 2, Sheep
-
72'-dihydroxy-3'4'-d...
72'-dihydroxy-3'4'-dimethoxyisoflavane-7-O-glucoside is a natural product from Astragalus membranaceus.
-
2-Aminothiazol-4-ace...
2-Aminothiazol-4-acetic acid is a chemical compound.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


