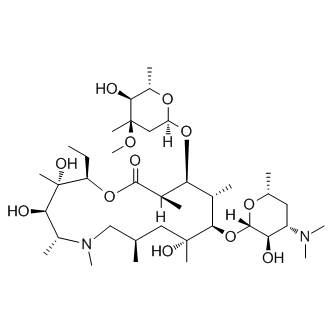
Azithromycin
CAS No. 83905-01-5
Azithromycin( CP 62993 )
Catalog No. M16114 CAS No. 83905-01-5
A macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 76 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 197 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAzithromycin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.
-
DescriptionA macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections; also attenuates myofibroblast differentiation and lung fibrosis development through proteasomal degradation of NOX4; also blocks autophagy by preventing lysosomal acidification.Bacterial Infection Approved(In Vitro):Azithromycin (2 μM) augments rhinovirus-induced IFNβ expression in primary bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatics, which is associated with over-expression of RIG-I like receptors and repression of viral replication. Knockdown of MDA5, but not knockdown of RIG-I, diminishes azithromycin (2 μM)-enhanced viral-induced IFNβ expression in asthmatic primary bronchial epithelial cells. Azithromycin specifically reduces MMP-9 mRNA and protein levels without affecting NF-κB in endotoxin-challenged monocytic THP-1 cells.(In Vivo):Azithromycin (50 mg/kg) has no effect on bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory parameters and LDH levels in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation. Azithromycin induces neither general inflammatory parameters nor LDH release in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation, and augments expression of interferon-stimulated genes and the pattern recognition receptor MDA5 but not RIG-I in exacerbating mice.
-
In VitroAzithromycin (2 μM) augments rhinovirus-induced IFNβ expression in primary bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatics, which is associated with over-expression of RIG-I like receptors and repression of viral replication. Knockdown of MDA5, but not knockdown of RIG-I, diminishes azithromycin (2 μM)-enhanced viral-induced IFNβ expression in asthmatic primary bronchial epithelial cells. Azithromycin specifically reduces MMP-9 mRNA and protein levels without affecting NF-κB in endotoxin-challenged monocytic THP-1 cells.
-
In VivoAzithromycin (50 mg/kg) has no effect on bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory parameters and LDH levels in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation. Azithromycin induces neither general inflammatory parameters nor LDH release in a mouse model of asthma exacerbation, and augments expression of interferon-stimulated genes and the pattern recognition receptor MDA5 but not RIG-I in exacerbating mice.
-
SynonymsCP 62993
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
Recptorproteinsynthesis
-
Research AreaInfection
-
IndicationBacterial Infection
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number83905-01-5
-
Formula Weight748.9845
-
Molecular FormulaC38H72N2O12
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESCC[C@@H]1[C@@]([C@@H]([C@H](N(C[C@@H](C[C@@]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C(=O)O1)C)O[C@H]2C[C@@]([C@H]([C@@H](O2)C)O)(C)OC)C)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@H](O3)C)N(C)C)O)(C)O)C)C)C)O)(C)O
-
Chemical Name1-Oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one, 13-[(2,6-dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-, (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Tsubouchi K, et al. Autophagy. 2017 Jun 14:1-15.
2. Moriya S, et al. Int J Oncol. 2013 May;42(5):1541-50.
3. Renna M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2011 Sep;121(9):3554-63.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ceftazidime Pentahyd...
Ceftazidime is a β-lactam antibacterial agent which has demonstrated a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria.
-
Proanthocyanidins(b)
Proanthocyanidins is a natural produceused as antioxidant and anti-cancers agent.?
-
Tolclofos-methyl
Tolclofos-methyl is an organophosphorus fungicide and widely utilized to control soil-borne diseases.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


