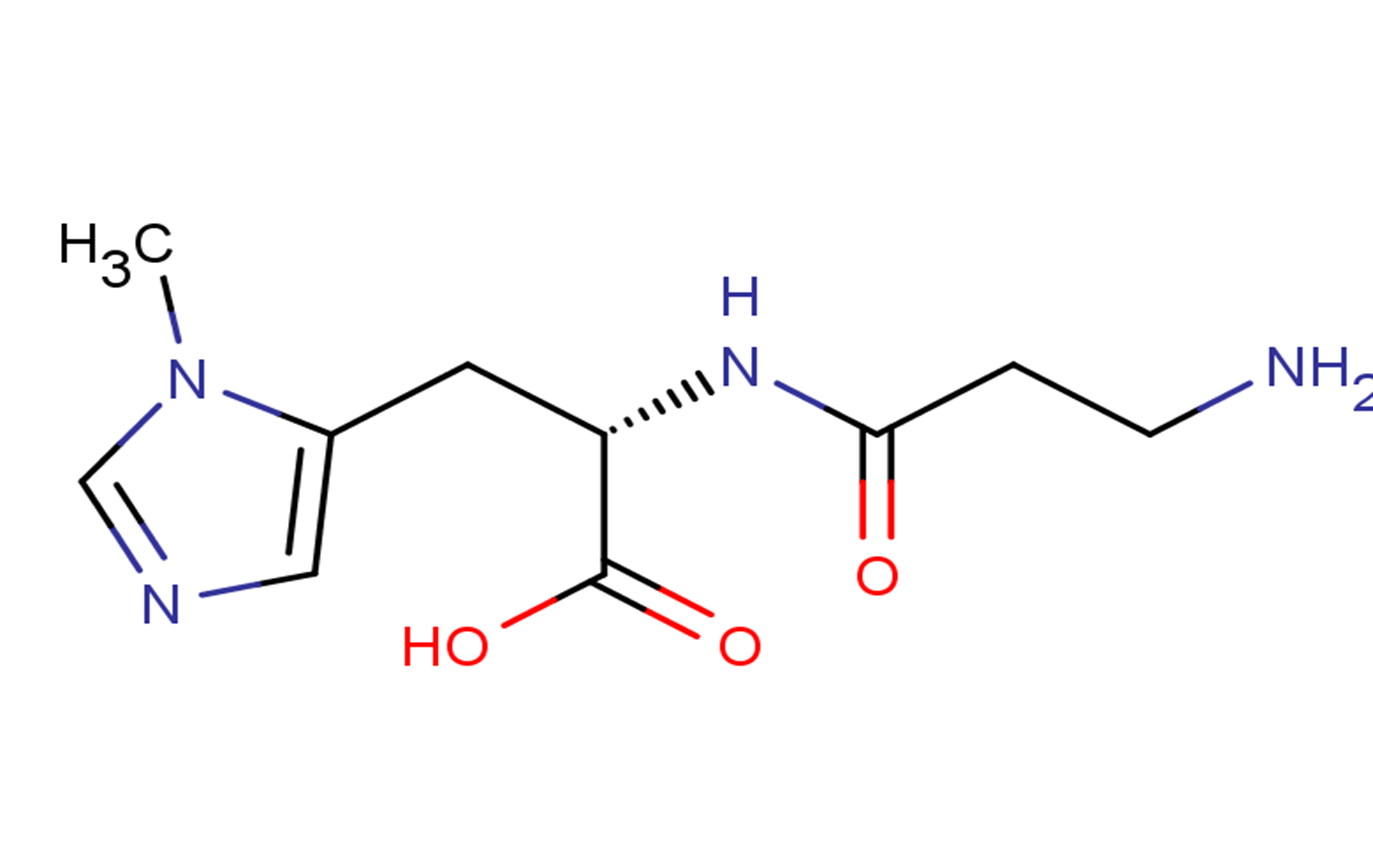
Anserine
CAS No. 584-85-0
Anserine( L-Anserine )
Catalog No. M24575 CAS No. 584-85-0
Anserine is a dipeptide containing β-alanine and histidine, which can be found in the skeletal muscle and brain of mammals and birds.?
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 200MG | 26 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAnserine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAnserine is a dipeptide containing β-alanine and histidine, which can be found in the skeletal muscle and brain of mammals and birds.?
-
DescriptionAnserine is a dipeptide containing β-alanine and histidine, which can be found in the skeletal muscle and brain of mammals and birds.?Anserine is not cleaved by serum carnosinase and act as biochemical buffers, chelators, antioxidants, and anti-glycation agents.?Anserine improves memory functions in Alzheimer's disease (AD)-model mice.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoAnserine (drinking water at a concentration of 2.0?g/L (equivalent to 10?mg/mouse); for 8 weeks) completely recoveres the memory deficits, improves pericyte coverage on endothelial cells in the brain, and diminishes chronic glial neuroinflammatory reactions in AβPPswe/PSEN1dE9 Alzheimer's disease (AD) model mice over 18-months old.
-
SynonymsL-Anserine
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number584-85-0
-
Formula Weight240.26
-
Molecular FormulaC10H16N4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Insoluble;Water:10 mM
-
SMILESO=C(O)[C@H](CC1=CN=CN1C)NC(CCN)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kubomura, Daiki, Matahira, et al. Effect of anserine ingestion on the hyperglycemia and autonomic nerves in rats and humans.[J]. Nutritional Neuroscience, 2010.
molnova catalog



related products
-
17-DIMETHYLXANTHINE
Paraxanthine is a metabolite of caffeine (sc-202514) which functions as an adenosine receptor ligand and a PARP-1 inhibitor in pulmonary epithelial cells.
-
5-Phenylvaleric Acid
5-Phenylvaleric acid is a pentanoic acid of bacterial origin occasionally found in human biofluids.
-
Zinc Protoporphyrin
Zinc Protoporphyrin is an orally active and competitive inhibitor of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and markedly attenuates the protective effects of Phloroglucinol (PG) against H2O2, and has anti-cancer activity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


