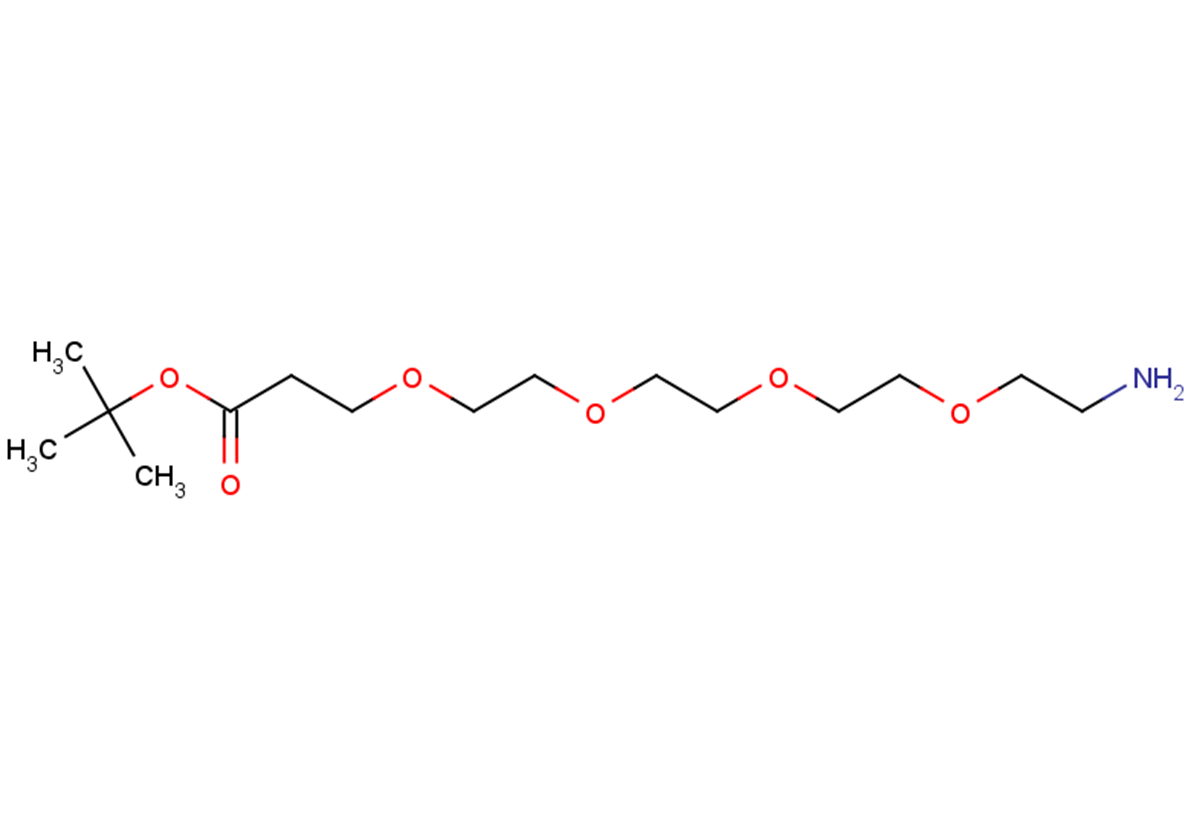
Amino-PEG4-Boc
CAS No. 581065-95-4
Amino-PEG4-Boc( —— )
Catalog No. M24572 CAS No. 581065-95-4
Amino-PEG4-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 26 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAmino-PEG4-Boc
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAmino-PEG4-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
DescriptionAmino-PEG4-Boc is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs.
-
In VitroPROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayPROTACs
-
TargetPROTAC
-
RecptorPEGs|Alkyl/ether
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number581065-95-4
-
Formula Weight321.41
-
Molecular FormulaC15H31NO6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(OC(C)(C)C)CCOCCOCCOCCOCCN
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.An S, et al. Small-molecule PROTACs: An emerging and promising approach for the development of targeted therapy drugs. EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:553-562
molnova catalog



related products
-
DADPS Biotin Azide
Biotin-PEG4-amino-t-Bu-DADPS-C6-azide is a PEGylated PROTAC linker suitable for PROTAC synthesis .
-
dBRD9
dBRD9 is a PROTAC that bridge the BRD9 bromodomain and the cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase complex.
-
DBCO-PEG5-NHS ester
DBCO-PEG5-NHS ester is a PROTAC linker belonging to the PEG and Alkyl/ether classes for the synthesis of a range of PROTAC molecules.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


