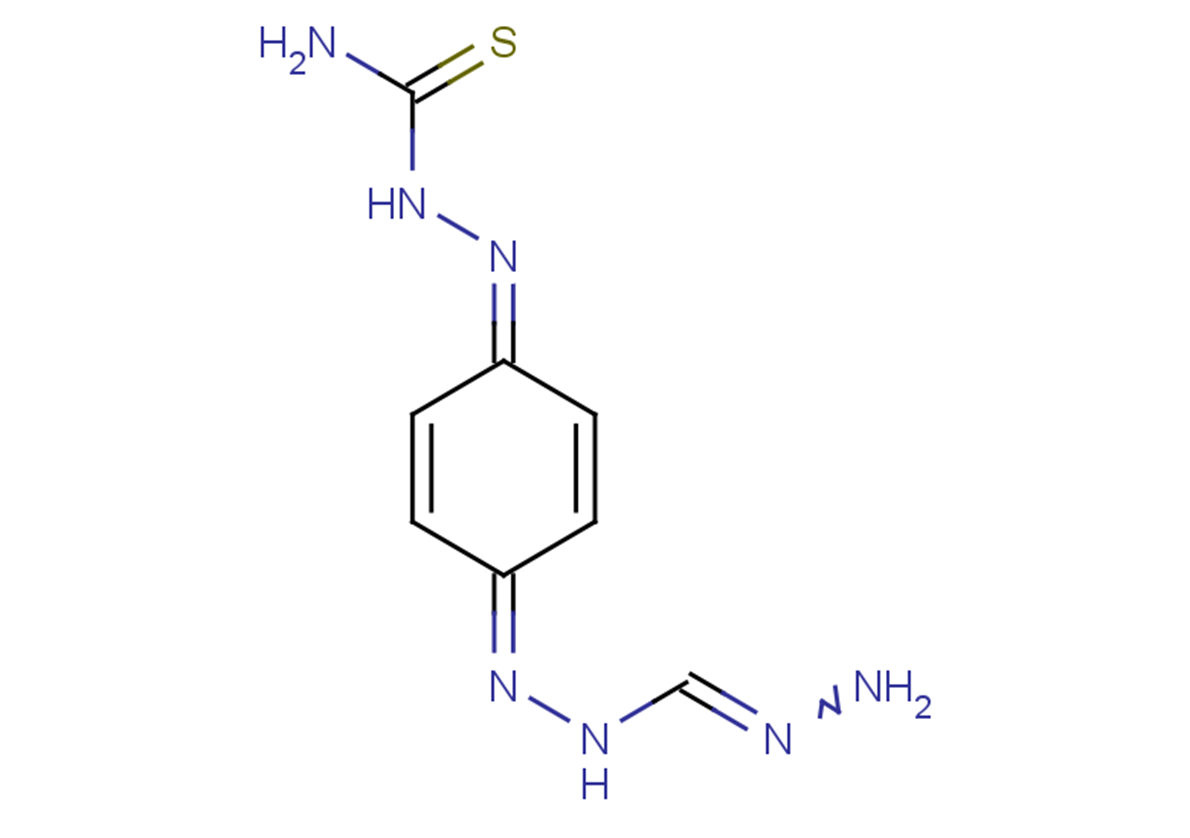
Ambazone
CAS No. 539-21-9
Ambazone( Ambazon | Primal )
Catalog No. M24525 CAS No. 539-21-9
Ambazone was found to be active against various transplantable tumors in mice as well as rats.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 57 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 81 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 147 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 211 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 313 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAmbazone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAmbazone was found to be active against various transplantable tumors in mice as well as rats.
-
DescriptionAmbazone was found to be active against various transplantable tumors in mice as well as rats.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAmbazon | Primal
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number539-21-9
-
Formula Weight237.29
-
Molecular FormulaC8H11N7S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:Soluble
-
SMILESNC(NN=C(C=C1)C=CC1=NNC=NN)=S
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.L?ber G, et al. Ambazone as a membrane active antitumor drug. Biophys Chem. 1990 Apr;35(2-3):287-300. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(90)80016-z. PMID: 2204445.
molnova catalog



related products
-
GNF4877
GNF4877 is a potent DYRK1A and GSK3β inhibitor (IC50s: 6?nM and 16?nM).
-
Neotame
Neotame is a white-colored, dipeptide methyl ester, which is found to be a highly potent and non-nutritive sweetener or flavour enhancer and hence finds applications in a variety of foods.
-
Carbaglu
Carglumic acid is an orphan drug used for the treatment of hyperammonaemia in patients with N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency. This rare genetic disorder results in elevated blood levels of ammonia, which can eventually cross the blood-brain barrier and cause neurologic problems, cerebral edema, coma, and death.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


