Abametapir
CAS No. 1762-34-1
Abametapir( HA-44 | BRN 0123183 )
Catalog No. M20813 CAS No. 1762-34-1
Abametapir a metalloproteinase inhibitor is able to target metalloproteinases critical to egg hatching and louse development.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAbametapir
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAbametapir a metalloproteinase inhibitor is able to target metalloproteinases critical to egg hatching and louse development.
-
DescriptionAbametapir a metalloproteinase inhibitor is able to target metalloproteinases critical to egg hatching and louse development.(In Vitro):Abametapir is capable of chelating heavy metal ions, including iron, copper, and zinc, and is therefore able to interact with a range of targets within the insect that require metal co-factors for function, including metalloproteinases.
-
In VitroAbametapir is capable of chelating heavy metal ions, including iron, copper, and zinc, and is therefore able to interact with a range of targets within the insect that require metal co-factors for function, including metalloproteinases.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsHA-44 | BRN 0123183
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptormetalloproteinases
-
Research AreaOthers
-
IndicationPediculosis
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1762-34-1
-
Formula Weight184.24
-
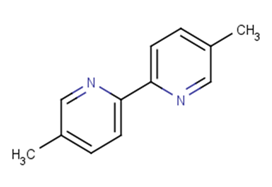
Molecular FormulaC12H12N2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:37mg/mL(200.83mM)
-
SMILESCc1ccc(-c2ccc(C)cn2)nc1
-
Chemical Name55'-dimethyl-22'-bipyridinyl
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Bowles VM Hanegraaf S Ahveninen T.et al.Effect of a New Head Lice Treatment Abametapir Lotion 0.74% on Louse Eggs: A Randomized Double-Blind Study.Glob Pediatr Health. 2019 Feb 22.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ulixertinib
Ulixertinib (BVD-523, VRT752271) is an effective and reversible ERK1/ERK2 inhibitor. The IC50 of Ulixertinib is less than 0.3 nM for ERK2.
-
Tetanus toxin (TT) p...
Tetanus toxin (TT) peptide
-
C3a (70-77) TFA (635...
C3a (70-77) TFA (Complement 3a (70-77) TFA) is a COOH-terminal fragment of the C3a anaphylatoxin peptide.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


