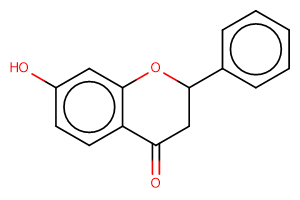
7-Hydroxyflavanone
CAS No. 6515-36-2
7-Hydroxyflavanone( —— )
Catalog No. M21308 CAS No. 6515-36-2
7-Hydroxyflavanone shows antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 75 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name7-Hydroxyflavanone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description7-Hydroxyflavanone shows antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates.
-
Description7-Hydroxyflavanone shows antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifection
-
RecptorAntifection
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6515-36-2
-
Formula Weight240.25
-
Molecular FormulaC15H12O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOc(cc1)cc(OC(C2)c3ccccc3)c1C2=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mikell J R Khan I A . Bioconversion of 7-Hydroxyflavanone: Isolation Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Twenty-One Phase I and Phase II Microbial Metabolites[J]. planta medica 2013 60(9):1139.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Hamamelitannin
Hamamelitannin a polyphenol extracted from the bark of Hamamelis virginiana, has cytotoxic and antibiofilm activities,and is a quorum-sensing (QS) inhibitor.
-
4-Acetamidobenzenesu...
4-Acetamidobenzenesulfonamide used in proteomics research and is an anti-infective agent.
-
Bacopasaponin C
Bacopasaponin C may have antioxidant activity, it also shows anti-leishmanial property.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


