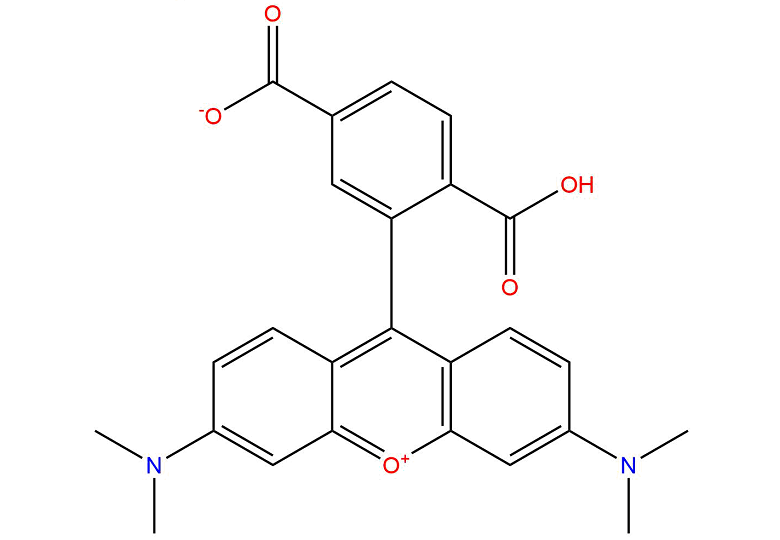
6-TAMRA
CAS No. 91809-67-5
6-TAMRA( 6-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine )
Catalog No. M24966 CAS No. 91809-67-5
6-TAMRA has been a widely used fluorophore for preparing bioconjugates, especially fluorescent antibody and avidin derivatives used in immunochemistry.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 104 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name6-TAMRA
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description6-TAMRA has been a widely used fluorophore for preparing bioconjugates, especially fluorescent antibody and avidin derivatives used in immunochemistry.
-
Description6-TAMRA has been a widely used fluorophore for preparing bioconjugates, especially fluorescent antibody and avidin derivatives used in immunochemistry.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms6-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number91809-67-5
-
Formula Weight430.45
-
Molecular FormulaC25H22N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:2.86 mg/mL (6.64 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESCN(C1=CC2=[O+]C3=C(C=CC(N(C)C)=C3)C(C4=CC(C([O-])=O)=CC=C4C(O)=O)=C2C=C1)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Lofendazam
Lofendazam (Bu 1014) is a benzodiazepine derivative that has sedative and anxiolytic effects.
-
Thymine
Thymine is found in the nucleic acid DNA. In RNA thymine is replaced with uracil in most cases. In DNA, thymine binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds to assist in stabilizing the nucleic acid structures.
-
NAV-2729
NAV-2729 inhibits six ArfGEFs (human ARNO, EFA6, BIG1, and BRAG2 and Legionella and Rickettsia RalF), the strongest effects being against BRAG2, Arf1 and Arf6.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


