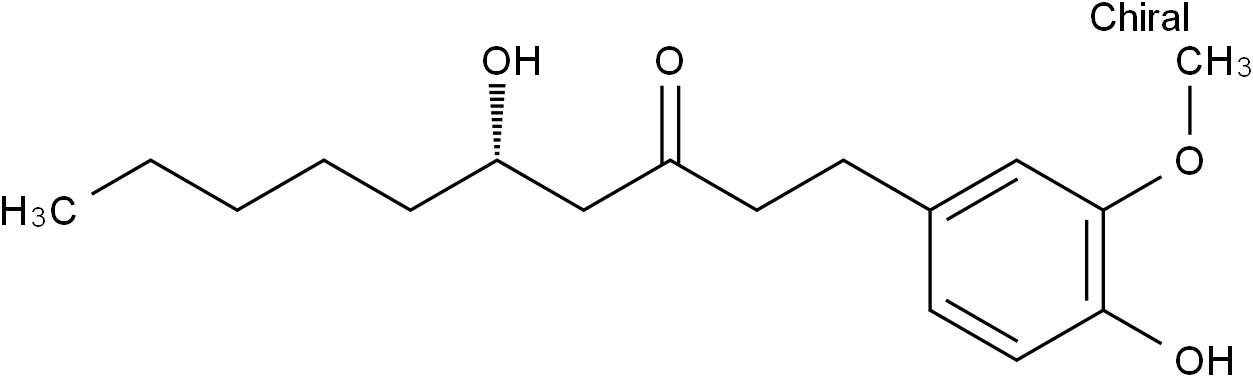
6-Gingerol
CAS No. 23513-14-6
6-Gingerol( 6-Gingerol )
Catalog No. M13674 CAS No. 23513-14-6
6-Gingerol may as an antioxidant to protect HL-60 cells from oxidative stress.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 59 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 98 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 158 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 290 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name6-Gingerol
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description6-Gingerol may as an antioxidant to protect HL-60 cells from oxidative stress.
-
Description6-Gingerol may as an antioxidant to protect HL-60 cells from oxidative stress. It has protective effects for Yous tumors in the bowel,breast tissue, ovaries,the pancreas,among other tissues.
-
In Vitro——
-
In VivoIn animal studies, -gingerol significantly ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by restoration of body weight loss, reduction in intestinal bleeding, and prevention of colon length shortening. In addition, -gingerol suppresses DSS-elevated production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFα, and IL-12).
-
Synonyms6-Gingerol
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number23513-14-6
-
Formula Weight294.4
-
Molecular FormulaC17H26O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc.
-
SMILESCCCCC[C@H](O)CC(CCC1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1)=O
-
Chemical Name(S)-5-hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-decanone
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Tzeng TF, et al. Phytomedicine. 2015 Apr 15;22(4):452-61.
molnova catalog



related products
-
DAAO inhibitor-1
DAAO inhibitor-1 is a potent D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitor (IC50: 0.12 μM).
-
Disperse Fast Yellow...
Disperse Fast Yellow 4K is a color additive used in dyes.
-
Kemptide
Kemptide is a synthetic heptapeptide, acting as a substrate for cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PK).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


