5-ROX
CAS No. 216699-35-3
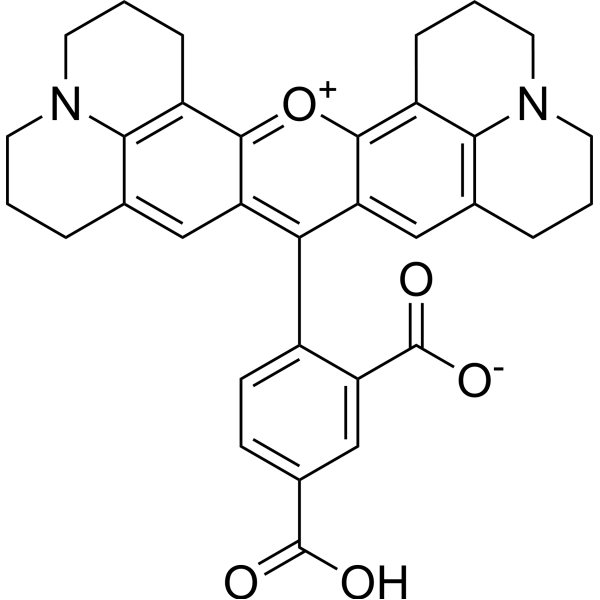
5-ROX( 5-Carboxy-X-rhodamine )
Catalog No. M27026 CAS No. 216699-35-3
5-ROX, a rhodamine dye, exhibits strong fluorescence property in aqueous buffer with the λexit of 580 nm (ε=3.6×10^4/(M·cm)), and λemit of 604 nm ( =0.94).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 43 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 69 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 114 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 210 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 357 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 524 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1107 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name5-ROX
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description5-ROX, a rhodamine dye, exhibits strong fluorescence property in aqueous buffer with the λexit of 580 nm (ε=3.6×10^4/(M·cm)), and λemit of 604 nm ( =0.94).
-
Description5-ROX, a rhodamine dye, exhibits strong fluorescence property in aqueous buffer with the λexit of 580 nm (ε=3.6×10^4/(M·cm)), and λemit of 604 nm ( =0.94).
-
In VitroRhodamine dyes are important because of their favorable photochemical and photophysical properties. They have long wavelength absorption maxima, high molar absorptivities, and high quantum yields.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms5-Carboxy-X-rhodamine
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorFungal
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number216699-35-3
-
Formula Weight534.612
-
Molecular FormulaC33H30N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (233.82 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)c1ccc(c(c1)C([O-])=O)-c1c2cc3CCCN4CCCc(c34)c2[o+]c2c3CCCN4CCCc(cc12)c34
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.L Kanetis, et al. Characterization of genetic and biochemical mechanisms of fludioxonil and pyrimethanil resistance in field isolates of Penicillium digitatum. Phytopathology
molnova catalog



related products
-
BR-1
BR-1 is a phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL-3) inhibitor which blocks the migration and invasion of metastatic cancer cells.
-
Proanthocyanidins
Extracted from Grape seed,pine bark coast of France; Suitability:Water,most organic solvents;Store the product in sealed,cool and dry condition.
-
Nimustine Hydrochlor...
Nimustine has been used in trials studying the treatment of Glioblastoma.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


