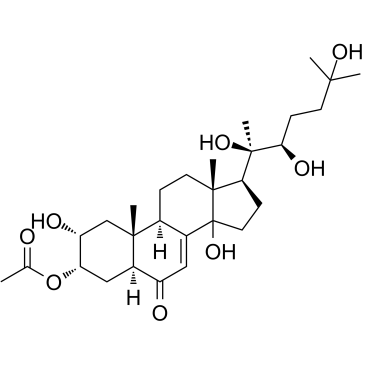
3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone
CAS No. 22961-68-8
3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone( —— )
Catalog No. M21779 CAS No. 22961-68-8
3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone is an steroid isolated from the roots of Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B.Clark.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 302 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 447 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 714 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1017 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone is an steroid isolated from the roots of Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B.Clark.
-
Description3-O-Acetyl-20-Hydroxyecdysone is an steroid isolated from the roots of Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B.Clark.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number22961-68-8
-
Formula Weight522.67
-
Molecular FormulaC??H??O?
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCC(C)(O)CC[C@@H](O)[C@](C)(O)[C@H]1CCC2(O)C3=CC([C@@]4([H])C[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@H](O)C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Schisantherin B
Schisantherin B shows good effect in lowering the serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase level of the patients suffering from chronic virus hepatitis.
-
22'-Cyclouridine
22'-Cyclouridine is a research tool for antiviral and anticancer studies.
-
Sotrovimab
Sotrovimab (VIR 7831) is a monoclonal antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


