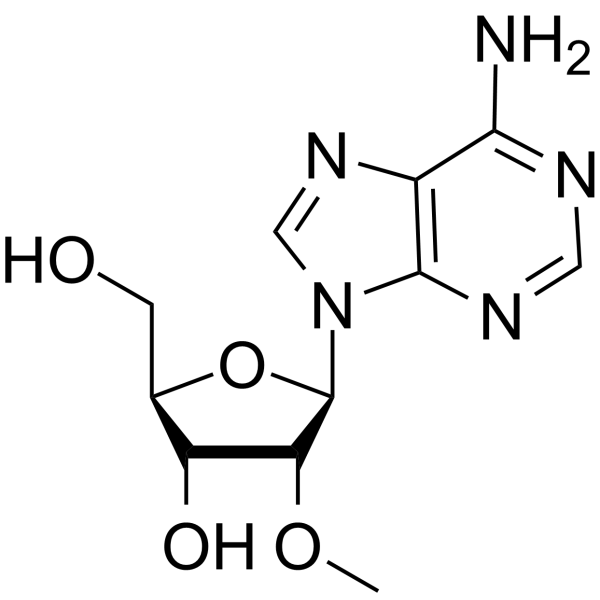
2-O-Methyladenosine
CAS No. 2140-79-6
2-O-Methyladenosine ( —— )
Catalog No. M26534 CAS No. 2140-79-6
2'-O-Methyladenosine, a methylated adenine residue is found in the urine of normals and adenosine deaminase deficient patients. It shows unique hypotensive activities.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 53 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 115 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 174 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 293 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-O-Methyladenosine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2'-O-Methyladenosine, a methylated adenine residue is found in the urine of normals and adenosine deaminase deficient patients. It shows unique hypotensive activities.
-
Description2'-O-Methyladenosine, a methylated adenine residue is found in the urine of normals and adenosine deaminase deficient patients. It shows unique hypotensive activities.(In Vivo):2'-O-Methyladenosine (100, 200 mg/kg, i.p., single dose) exhibits unique hypotensive activities in rats .
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2140-79-6
-
Formula Weight281.3
-
Molecular FormulaC11H15N5O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESOC[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@H]([C@H](N2C=NC3=C(N=CN=C32)N)O1)OC)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.J J Turner, et al. Krypton Fluoride: Preparation by the Matrix Isolation Technique. Science. 1963 May 31;140(3570):974-5.
molnova catalog


related products
-
Indole-3-carboxaldeh...
1H-Indole-3-carboxaldehyde also known as 3-formylindole or 3-indolealdehyde belongs to the class of organic compounds known as indoles. Indoles are compounds containing an indole moiety which consists of pyrrole ring fused to benzene to form 23-benzopyrrole.
-
Propylparaben
Propylparaben is an antimicrobial agent preservative flavouring agent.
-
D-DELTA-TOCOPHEROL
D-DELTA-TOCOPHEROL is an isomer of Vitamin Ehas antioxidant activityand might be useful as effective ingredients in whitening cosmetics with lower skin toxicity.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


