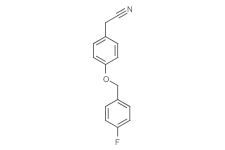
2-(4-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)phenyl)acetonitrile
CAS No. 1016535-83-3
2-(4-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)phenyl)acetonitrile( Oct3/4-inducer-1, MDK35833 | MDK-35833 )
Catalog No. M17751 CAS No. 1016535-83-3
Detail unknown.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 259 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 478 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 691 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 963 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-(4-(4-methoxybenzyloxy)phenyl)acetonitrile
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDetail unknown.
-
DescriptionMDK35833, also known as Oct3/4-inducer-1, is a potent Oct3/4-inducer. MDK35833 can promot expression and stabilization of Oct3/4 and enhance its transcriptional activity in diverse human somatic cells, implying the possible benefit from using this class of compounds in regenerative medicine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsOct3/4-inducer-1, MDK35833 | MDK-35833
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetTyrosinase
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1016535-83-3
-
Formula Weight241.26
-
Molecular FormulaC15H12FNO
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (414.49 mM)
-
SMILESc1cc(ccc1CC#N)OCc1ccc(cc1)F
-
Chemical Name4-[(4-Fluorophenyl)methoxy]-benzeneacetonitrile
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
3',4'-Dihydroxyaceto...
3', 4'-Dihydroxyacetophenone is an active constituent of Chinese medicine. It is platelet aggregation Inhibitor and also has anti-arrhythmia activity.
-
KN-93
KN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase.
-
Benzoyloxypeoniflori...
Benzoyloxypeoniflorin is a natural productcontributes to improving blood circulation through their inhibitory effects on both platelet aggregation and blood coagulation.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


