17-DIMETHYLXANTHINE
CAS No. 611-59-6
17-DIMETHYLXANTHINE( Paraxanthine )
Catalog No. M19728 CAS No. 611-59-6
Paraxanthine is a metabolite of caffeine (sc-202514) which functions as an adenosine receptor ligand and a PARP-1 inhibitor in pulmonary epithelial cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 51 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 77 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 109 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 161 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name17-DIMETHYLXANTHINE
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionParaxanthine is a metabolite of caffeine (sc-202514) which functions as an adenosine receptor ligand and a PARP-1 inhibitor in pulmonary epithelial cells.
-
DescriptionParaxanthine is a metabolite of caffeine (sc-202514) which functions as an adenosine receptor ligand and a PARP-1 inhibitor in pulmonary epithelial cells. Studies suggest that Paraxanthine is structurally similar to caffeine and possibly mediates the physiological effects of caffeine. Also Paraxanthine acts as a competitive phosphodiesterase inhibitor which increases intracellular cAMP activates PKA inhibits TNF-α and leukotriene synthesis. In addition Paraxanthine acts as a Na+/K+ ATPase enzymatic effector.
-
In VitroWhen Paraxanthine (PX) is applied to the cultures for a prolonged period, the number of TH+neurons is augmented in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of Paraxanthine, already significant at 100 μM, increases gradually and remains optimal between 800 and 1000 μM, at 10 DIV. Counts of TH+neurons performs at different stages of maturation of the cultures indicate that Paraxanthine most likely prevents DA cell loss. GDNF, a prototypical trophic factor for DA neurons, is only slightly more effective than 800 μM Paraxanthine in rescuing DA neurons after 10 and 16 DIV when used at an optimal concentration of 20 ng/mL. About 80% of caffeine is N3-demethylated to form Paraxanthine, Unlike Paraxanthine, caffeine is poorly effective in protecting DA neurons from death For example, at a concentration of 800 μM, caffeine produces only a modest 40% increase in the number of TH+ cells at 10 DIV, whereas the same concentration of Paraxanthine optimally promotes DA cell survival (169% increase).
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsParaxanthine
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number611-59-6
-
Formula Weight180.16
-
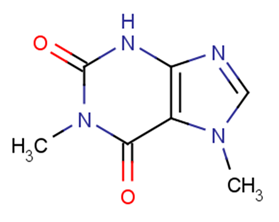
Molecular FormulaC7H8N4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM;Water:1mg/mL
-
SMILESCn1cnc2[nH]c(=O)n(C)c(=O)c12
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Jiang M Kameda K Han L K et al. Isolation of lipolytic substances caffeine and 17-dimethylxanthine from the stem and rhizome of Sinomenium actum[J]. Planta Medica 1998 64(04):375-377.
molnova catalog



related products
-
2,6-Dibromophenol
2,6-Dibromophenol is extracted from the skin and muscle of flatfish.
-
Ethyl nonanoate
Ethyl nonanoate (Ethyl pelargonate) is an abundant ester in spirits, and its presence is usually associated with the aroma of alcoholic beverages.
-
1-Methyladenosine
1-Methyladenosine (M1A) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine nucleosides.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


