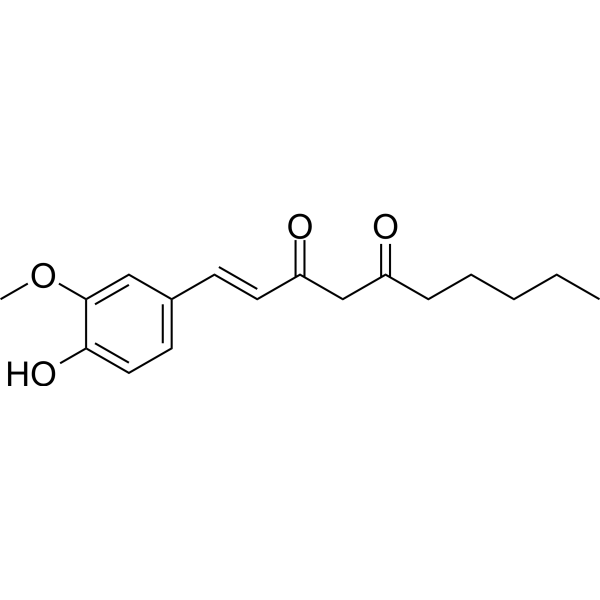
1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione
CAS No. 76060-35-0
1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione( —— )
Catalog No. M31246 CAS No. 76060-35-0
1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione is a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione is a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
-
Description1-Dehydro-6-gingerdione is a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
-
In Vitro6-Dehydrogingerdione could trigger apoptotic cell death via both mitochondrial- and Fas receptor-mediated pathways.6-Dehydrogingerdione (6-DG) up-regulates Ser-15 phosphorylation and evoked p53 nuclear translocation.6-Dehydrogingerdione (6-DG) induces mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis Analysis Cell Line:Hep G2 cells.Concentration:0, 50, 100 μM.Incubation Time:24 h.Result:Induced Apoptosis in Hep G2 Cells.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number76060-35-0
-
Formula Weight290.4
-
Molecular FormulaC17H22O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Neuromedin (U25), hu...
Neuromedin U-25 human is the active form of neuromedin U in human. Neuromedin U-25 human inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, which leads to early-onset obesity. Neuromedin U-25 serves as vasoconstrictor in human vascular beds.
-
Guibourtinidin chlor...
Reference standards.
-
Cixutumumab
Cixutumumab (IMC-A12), a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting IGF-1R, exhibits high affinity and inhibits ligand-dependent receptor activation, impeding downstream signaling.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


