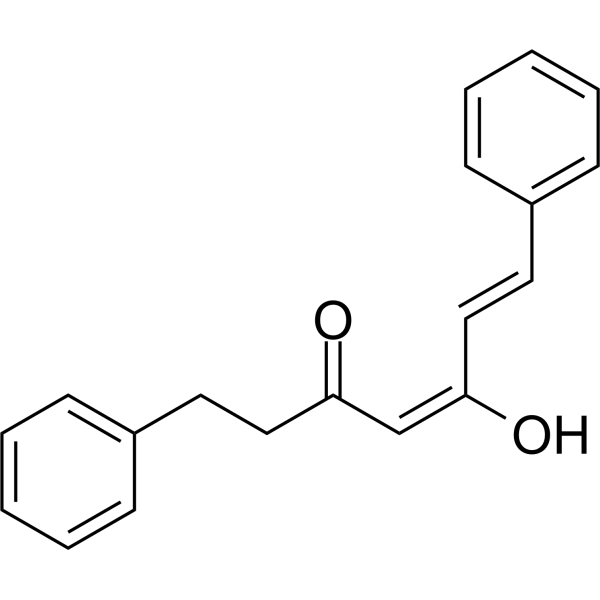
1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one
CAS No. 87095-77-0
1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one( —— )
Catalog No. M31918 CAS No. 87095-77-0
1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one is a natural product of Alpinia, Zingiberaceae. 1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one can be used as a reference standard.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 630 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one is a natural product of Alpinia, Zingiberaceae. 1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one can be used as a reference standard.
-
Description1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one is a natural product of Alpinia, Zingiberaceae. 1,7-Diphenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6-hepten-3-one can be used as a reference standard.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number87095-77-0
-
Formula Weight278.4
-
Molecular FormulaC19H18O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
UUN44923
UUN44923 is a FTO inhibitor.?It may be useful for treating diseases assocd.?with FTO targets, obesity, metabolic syndrome (MS) , type 2 diabetes (T2D) , Alzheimer's diseases, breast cancers, small- cell lung cancers, a human bone marrow striated muscle cancer, a pancreatic cancer, malignant glioblastoma and the like.?
-
6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-...
6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-glucoside is derived from Tanacetum parthenium and T. vulgare showing anti-inflammatory effects.
-
CX-6258 HCl
CX-6258 HCl is an effective, orally efficacious Pim1/2/3 kinase inhibitor (IC50: 5/25/16 nM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


