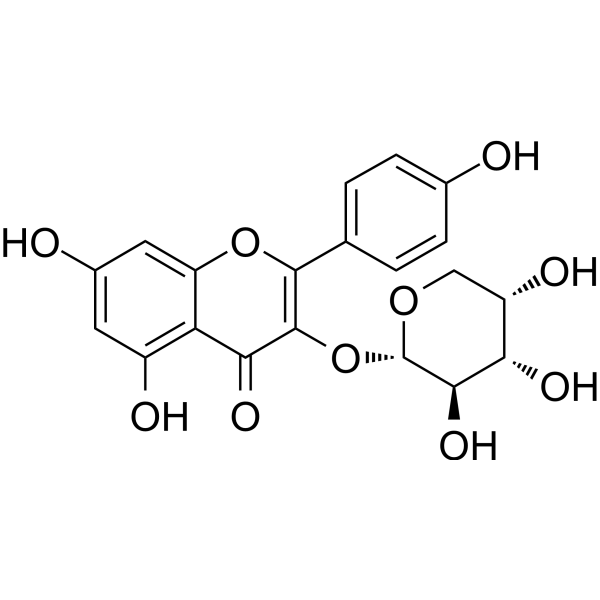
Kaempferol 3-O-arabinoside
CAS No. 99882-10-7
Kaempferol 3-O-arabinoside( —— )
Catalog No. M31106 CAS No. 99882-10-7
Kaempferol-3-O-α±-D-arabinoside displays cytotoxic and high antioxidant activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 769 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameKaempferol 3-O-arabinoside
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKaempferol-3-O-α±-D-arabinoside displays cytotoxic and high antioxidant activity.
-
DescriptionKaempferol-3-O-α±-D-arabinoside displays cytotoxic and high antioxidant activity.Kaempferol-3-O-arabinoside and kaempferol-3-O-glucoside can function as antioxidants in biological systems, particularly skin exposed to UV radiation by scavenging ROS, and protect cellular membrane against ROS; they can be applicable to new cosmeceuticals for antioxidant, antiaging, and antibacterial activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number99882-10-7
-
Formula Weight418.4
-
Molecular FormulaC20H18O10
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
SV40 large T antigen...
SV40 large T antigen NLS is from Large T antigen residue 47 to 55, enables protein import into cell nucleus. This peptide is generated from Large T antigen residue 47 to 55.
-
Piperazine, 1-(4-flu...
Piperazine, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)methyl]- is a piperazine derivative.
-
Sitagliptin Intermed...
Sitagliptin Intermediate 2 is a useful organic compound that has been used in life science related research.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


